Mucosal immunity to asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection is associated with a peak intestinal anti-lectin immunoglobulin A antibody response
- PMID: 16790762
- PMCID: PMC1489685
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02018-05
Mucosal immunity to asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection is associated with a peak intestinal anti-lectin immunoglobulin A antibody response
Abstract
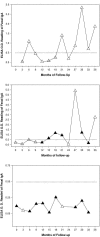
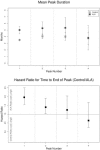
We monitored 93 subjects cured of amebic liver abscess (ALA) and 963 close associate controls in Durban, South Africa, and determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that the intestinal immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody response to the Entamoeba histolytica galactose-inhibitable adherence lectin is most accurately represented by a complex pattern of transitory peaks. One or more intestinal anti-lectin IgA antibody peaks occurred in 85.9% of ALA subjects over 36 months compared to 41.6% of controls (P < 0.0001). ALA subjects exhibited a greater number of anti-lectin IgA antibody peaks (P < 0.0001) than controls. In addition, their peak optical density values were higher (peak numbers 1 to 3, P < 0.003), peaks were of longer duration (for peaks 1 and 2, P </= 0.0054), and there was a shorter time interval between peaks (between 1 and 2 or 2 and 3, P </= 0.0106) than observed for control subjects. A prior E. histolytica infection was associated with the occurrence of an anti-lectin IgA antibody peak (79.1%, P < 0.0001) more so than for Entamoeba dispar infection (57.2%, P < 0.001). The annual number of anti-lectin IgA antibody peaks in ALA subjects was 0.71 per year, compared to just 0.22 in controls (P<0.0001), indicating a higher rate of exposure to the parasite than previously appreciated. Anti-lectin IgA antibody peaks were of higher amplitude following a E. histolytica infection compared to E. dispar (P = 0.01) and, for either, were of greater height in ALA subjects than controls (P < 0.01). ALA subjects demonstrated greater clearance of amebic infection after an anti-lectin IgA antibody peak compared to controls, and only 14.3% remained with a positive culture after the peak, compared to 38.9% in controls (P = 0.035). In summary, this prospective controlled longitudinal study elucidated the dynamic nature of the human intestinal IgA antibody response to E. histolytica and E. dispar infection and revealed that ALA subjects exhibit heightened intestinal anti-lectin IgA antibody peaks that are associated with clearance of E. histolytica and E. dispar infection.
Figures

References
-
- Abd-Alla, M. D., and J. I. Ravdin. 2005. Mucosal immune response to parasitic infections, p. 815-829. In J. Mestecky (ed.), Mucosal immunology, 3rd ed. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
-
- Abd-Alla, M. D., and J. I. Ravdin. 2000. Comparison of antigen captures ELISA to stool culture in methods for detection of asymptomatic Entamoeba species infection in Kafer Daoud, Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 62:579-582. - PubMed
-
- Abd-Alla, M. D., A. Wahib, and J. I. Ravdin. 2002. Diagnosis of amoebic colitis by antigen capture ELISA in patients presenting with acute diarrhea in Cairo, Egypt. Trop. Med. Int. Health 7:365-370. - PubMed
-
- Abo-El-Maged, I., G. Soong, A. El-Hawey, and J. I. Ravdin. 1996. Humoral and mucosal IgA antibody response to a recombinant 52-kDa cysteine-rich portion of the Entamoeba histolytica galactose-inhibitable lectin correlates with detection of native 170-kDa antigen in serum patients with amebic colitis. J. Infect. Dis. 174:157-162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

