The Yersinia enterocolitica invasin protein promotes major histocompatibility complex class I- and class II-restricted T-cell responses
- PMID: 16790806
- PMCID: PMC1489713
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00260-06
The Yersinia enterocolitica invasin protein promotes major histocompatibility complex class I- and class II-restricted T-cell responses
Abstract
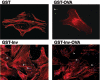
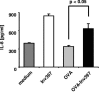
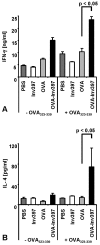
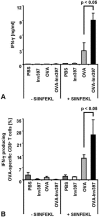
Yersinia enterocolitica invasin (Inv) protein confers internalization into and expression of proinflammatory cytokines by host cells. Both events require binding of Inv to beta1 integrins, which initiates signaling cascades including activation of focal adhesion complexes, Rac1, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and NF-kappaB. Here we tested whether Inv might be suitable as a delivery molecule and adjuvant if used as a component of a vaccine. For this purpose, hybrid proteins composed of Inv and ovalbumin (OVA) were prepared, applied as a coating to microparticles, and used for vaccination. Fusion of OVA to Inv did not significantly disturb the ability of Inv to promote host cell binding, internalization, and interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion when applied as a coating to microparticles. The microparticles were used for vaccination of mice adoptively transferred with OVA-specific T cells from OT-1 or DO11.10 mice. Administration of OVA-Inv-coated microparticles induced OVA-specific T-cell responses. OVA-specific CD4 T cells produced both gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and IL-4 as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Likewise, pronounced OVA-specific CD8 T-cell responses associated with IFN-gamma production were observed. Together, these results suggest that Inv might be an attractive tool in vaccination as it confers both host cell uptake and adjuvant activity by engagement of beta1 integrins of host cells, which leads to CD4 as well as CD8 T-cell responses.
Figures

References
-
- Ackerman, A. L., and P. Cresswell. 2004. Cellular mechanisms governing cross-presentation of exogenous antigens. Nat. Immunol. 5:678-684. - PubMed
-
- Alrutz, M. A., A. Srivastava, K. W. Wong, C. D'Souza-Schorey, M. Tang, L. E. Ch'Ng, S. B. Snapper, and R. R. Isberg. 2001. Efficient uptake of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis via integrin receptors involves a Rac1-Arp 2/3 pathway that bypasses N-WASP function. Mol. Microbiol. 42:689-703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

