Role of calcineurin in stress resistance, morphogenesis, and virulence of a Candida albicans wild-type strain
- PMID: 16790813
- PMCID: PMC1489686
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00142-06
Role of calcineurin in stress resistance, morphogenesis, and virulence of a Candida albicans wild-type strain
Abstract
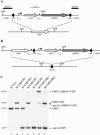
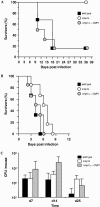
By generating a calcineurin mutant of the Candida albicans wild-type strain SC5314 with the help of a new recyclable dominant selection marker, we confirmed that calcineurin mediates tolerance to a variety of stress conditions but is not required for the ability of C. albicans to switch to filamentous growth in response to hypha-inducing environmental signals. While calcineurin was essential for virulence of C. albicans in a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis, deletion of CMP1 did not significantly affect virulence during vaginal or pulmonary infection, demonstrating that the requirement for calcineurin for a successful infection depends on the host niche.
Figures
References
-
- Cochran, W. G. 1950. Estimation of bacterial densities by means of the “most probable number.” Biometrics 6:105-116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

