Activation-associated phenotype of CD3 T cells in acute graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 16792671
- PMCID: PMC1942002
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03104.x
Activation-associated phenotype of CD3 T cells in acute graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
During the effector phase of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) response, donor T cells play an essential role and they are believed to change the expression of activation and co-stimulatory markers associated with functional alloreactivity. We analysed the expression of CD25, CD69, HLA-DR, CD154 and CD134 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry during acute GvHD (aGvHD) in 24 patients receiving human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-identical stem cell transplants. Expression of these molecules in nine patients with stages I-IV aGvHD was compared with 15 patients without aGvHD (n = 15). Serial analysis showed that peripheral blood of aGvHD patients presented a significant increase of CD4+ CD25+ cells (P < 0.03), CD4+ CD69+ (P < 0.04) and CD4+ CD134+ cells (P < 0.01). Additionally, there was a significant increase in CD8+ cells expressing CD134 (P = 0.007) and CD154 (P = 0.02). After resolution of aGvHD, the increased expression of these molecules returned to values comparable to patients without aGvHD. Only two of the 15 patients without clinical signs of aGvHD presented activated T cells that could not be attributed to development of aGvHD. In summary, our data show that multiple activation molecules are preferentially up-regulated on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from patients with aGvHD. These patients had a significant increase in the expression of the co-stimulatory molecules CD134 and CD154.
Figures
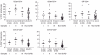
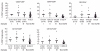
Similar articles
-
Expression of T cell activation antigen CD134 (OX40) has no predictive value for the occurrence or response to therapy of acute graft-versus-host disease in partial T cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999 May;23(10):1013-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1701755. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10373067
-
Kinetic of regulatory CD25high and activated CD134+ (OX40) T lymphocytes during acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Br J Haematol. 2004 Sep;126(5):697-703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05108.x. Br J Haematol. 2004. PMID: 15327522
-
CD25 expression distinguishes functionally distinct alloreactive CD4 CD134 (OX40) T-cell subsets in acute graft-versus-host disease.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004 May;10(5):298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2003.12.302. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004. PMID: 15111929
-
[CD4+, CD25+ regulatory T-lymphocytes: current concepts and therapeutic potential].J Soc Biol. 2002;196(4):263-6. J Soc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12645292 Review. French.
-
Antibodies to OX-40 (CD134) can identify and eliminate autoreactive T cells: implications for human autoimmune disease.Mol Med Today. 1998 Feb;4(2):76-83. doi: 10.1016/S1357-4310(97)01181-7. Mol Med Today. 1998. PMID: 9547794 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo expansion of co-transplanted T cells impacts on tumor re-initiating activity of human acute myeloid leukemia in NSG mice.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e60680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060680. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23585844 Free PMC article.
-
Human Herpesvirus-6B Reactivation Is a Risk Factor for Grades II to IV Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Nov;24(11):2324-2336. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.04.021. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29684567 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering T cells to suppress acute GVHD and leukemia relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Blood. 2023 Mar 9;141(10):1194-1208. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016052. Blood. 2023. PMID: 36044667 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed death-1 controls T cell survival by regulating oxidative metabolism.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):5789-800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402180. Epub 2015 May 13. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25972478 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CMV-IgG positivity of donors is beneficial for alloHSCT recipients with respect to the better short-term immunological recovery and high level of CD4+CD25high lymphocytes.Viruses. 2015 Mar 23;7(3):1391-408. doi: 10.3390/v7031391. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25807050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka J, Asaka M, Imamura M. T cell co-signalling molecules in graft-versus-host disease. Ann Hematol. 2000;79:283–90. - PubMed
-
- Dumont-Girard F, Roux E, van Lier RA, et al. Reconstitution of the T cell compartment after bone marrow transplantation: restoration of the repertoire by thymic emigrants. Blood. 1998;92:4464–71. - PubMed
-
- Herrera C, Torres A, Garcia-Castellano JM, et al. Prevention of graft-versus-host disease in high risk patients by depletion of CD4+ and reduction of CD8+ lymphocytes in the marrow graft. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;23:443–50. - PubMed
-
- Nagler A, Condiotti R, Nabet C, et al. Selective CD4+ T cell depletion does not prevent graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1998;66:138–41. - PubMed
-
- Hale G, Bright S, Chumbley G, et al. Removal of T cells from bone marrow for transplantation: a monoclonal antilymphocyte antibody that fixes human complement. Blood. 1983;62:873–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

