Screening in a spirit haunted world
- PMID: 16793529
- PMCID: PMC1524586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.05.014
Screening in a spirit haunted world
Abstract
High-throughput screening (HTS) campaigns can be dominated by hits that ultimately turn out to be non-drug-like. These "nuisance" compounds often behave strangely, with steep dose-response curves, absence of clear structure-activity relationships, and high sensitivity to assay conditions. Several mechanisms contribute to these artifacts, including chemically reactive molecules, those that absorb light in assays and those that affect redox conditions. One of the most common mechanisms behind artifactual inhibition is discussed in this review: at micromolar concentrations organic molecules can aggregate to form particles in aqueous buffers, and these aggregates can sequester and thereby inhibit protein targets. Aggregation-based inhibition is baffling from a chemical perspective, but viewed biophysically such behavior is expected. The range of molecules that behave this way, their rapid detection in a screening environment and their possible biological implications will be considered here.
Figures
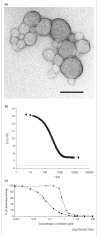
References
-
- Lipinski CA, et al. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997;46:3–26. - PubMed
-
- Rishton GM. Reactive compounds and in vitro false positives in HTS. Drug Discov. Today. 1997;2:382–384.
-
- Walters W, Namchuk M. Designing screens: how to make your hits a hit. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003;2:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Veber DF, et al. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:2615–2623. - PubMed
-
- Hajduk PJ, et al. Druggability indices for protein targets derived from NMR-based screening data. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:2518–2525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

