Kiss1 neurons in the forebrain as central processors for generating the preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge
- PMID: 16793876
- PMCID: PMC6673844
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1618-06.2006
Kiss1 neurons in the forebrain as central processors for generating the preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge
Abstract
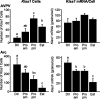
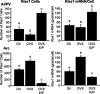
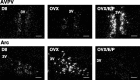
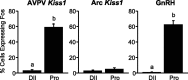
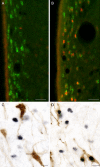
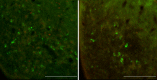
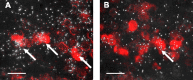
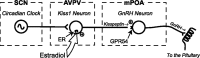
Kisspeptins are neuropeptides encoded by the Kiss1 gene, which have been implicated in the neuroendocrine regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion. The goal of this study was to test the hypothesis that activation of Kiss1 neurons in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) is linked to the induction of the preovulatory luteinizing hormone (LH) surge in the rat. First, we determined that levels of Kiss1 mRNA in the AVPV peaked during the evening of proestrus, whereas Kiss1 mRNA in the arcuate nucleus (Arc) was at its nadir. Second, we corroborated this observation by demonstrating that Kiss1 mRNA is increased in the AVPV at the time of an estrogen (E)- and progesterone-induced LH surge in ovariectomized animals, whereas in the Arc, the expression of Kiss1 mRNA was decreased. Third, we found that most Kiss1 neurons in the AVPV coexpress the immediate early gene Fos coincidently with the LH surge, but virtually none coexpressed Fos on diestrus. In contrast, Kiss1 neurons in the Arc were Fos negative at the time of the LH surge as well as on diestrus. Finally, we found that most Kiss1 neurons in the AVPV and Arc express estrogen receptor alpha mRNA, suggesting that E acts directly on these neurons. These results suggest that Kiss1 neurons in the AVPV play an active role in mediating the effects of E on the generation of the preovulatory GnRH/LH surge on proestrus.
Figures
References
-
- Barbacka-Surowiak G, Surowiak J, Stoklosowa S (2003). The involvement of suprachiasmatic nuclei in the regulation of estrous cycles in rodents. Reprod Biol 3:99–129. - PubMed
-
- Barraclough CA (1961). Production of anovulatory, sterile rats by single injections of testosterone propionate. Endocrinology 68:62–67. - PubMed
-
- Berghorn KA, Bonnett JH, Hoffman GE (1994). cFos immunoreactivity is enhanced with biotin amplification. J Histochem Cytochem 42:1635–1642. - PubMed
-
- Berghorn KA, Le WW, Sherman TG, Hoffman GE (2001). Suckling stimulus suppresses messenger RNA for tyrosine hydroxylase in arcuate neurons during lactation. J Comp Neurol 438:423–432. - PubMed
-
- Brailoiu GC, Dun SL, Ohsawa M, Yin D, Yang J, Chang JK, Brailoiu E, Dun NJ (2005). KiSS-1 expression and metastin-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 481:314–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
