Treatment with an estrogen receptor alpha ligand is neuroprotective in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 16793889
- PMCID: PMC6673842
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0453-06.2006
Treatment with an estrogen receptor alpha ligand is neuroprotective in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
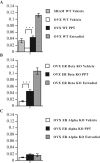
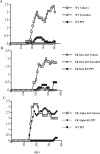
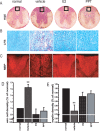
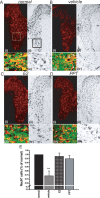
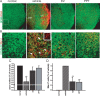
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory, neurodegenerative disease for which experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a model. Treatments with estrogens have been shown to decrease the severity of EAE through anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Here we investigated whether treatment with an estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) ligand could recapitulate the estrogen-mediated protection in clinical EAE. We then went on to examine both anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective mechanisms. EAE was induced in wild-type, ERalpha-, or ERbeta-deficient mice, and each was treated with the highly selective ERalpha agonist, propyl pyrazole triol, to determine the effect on clinical outcomes, as well as on inflammatory and neurodegenerative changes. ERalpha ligand treatment ameliorated clinical disease in both wild-type and ERbeta knock-out mice, but not in ERalpha knock-out mice, thereby demonstrating that the ERalpha ligand maintained ERalpha selectivity in vivo during disease. ERalpha ligand treatment also induced favorable changes in autoantigen-specific cytokine production in the peripheral immune system [decreased TNFalpha, interferon-gamma, and interleukin-6, with increased interleukin-5] and decreased CNS white matter inflammation and demyelination. Interestingly, decreased neuronal staining [NeuN+ (neuronal-specific nuclear protein)/beta3-tubulin+/Nissl], accompanied by increased immunolabeling of microglial/monocyte (Mac 3+) cells surrounding these abnormal neurons, was observed in gray matter of spinal cords of EAE mice at the earliest stage of clinical disease, 1-2 d after the onset of clinical signs. Treatment with either estradiol or the ERalpha ligand significantly reduced this gray matter pathology. In conclusion, treatment with an ERalpha ligand is highly selective in vivo, mediating both anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in EAE.
Figures
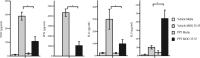
References
-
- Abramsky O (1994). Pregnancy and multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36:Suppl, S38–S41. - PubMed
-
- Aktas O, Smorodchenko A, Brocke S, Infante-Duarte C, Topphoff US, Vogt J, Prozorovski T, Meier S, Osmanova V, Pohl E, Bechmann I, Nitsch R, Zipp F (2005). Neuronal damage in autoimmune neuroinflammation mediated by the death ligand TRAIL. Neuron 46:421–432. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shammri S, Rawoot P, Azizieh F, AbuQoora A, Hanna M, Saminathan TR, Raghupathy R (2004). Th1/Th2 cytokine patterns and clinical profiles during and after pregnancy in women with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 222:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GL, Limacher M, Assaf AR, Bassford T, Beresford SA, Black H, Bonds D, Brunner R, Brzyski R, Caan B, Chlebowski R, Curb D, Gass M, Hays J, Heiss G, Hendrix S, Howard BV, Hsia J, Hubbell A, Jackson R, et al (2004). Effects of conjugated equine estrogen in postmenopausal women with hysterectomy: the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291:1701–1712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
