Chronic ethanol feeding suppresses beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated lipolysis in adipocytes isolated from epididymal fat
- PMID: 16794014
- PMCID: PMC1764504
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2006-0120
Chronic ethanol feeding suppresses beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated lipolysis in adipocytes isolated from epididymal fat
Abstract
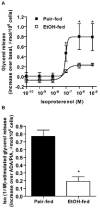
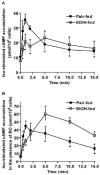
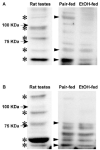
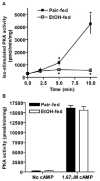
Chronic ethanol consumption disrupts G protein-dependent signaling pathways in rat adipocytes. Because lipolysis in adipocytes is regulated by G protein-mediated cAMP signal transduction, we hypothesized that cAMP-regulated lipolysis may be vulnerable to long-term ethanol exposure. Male Wistar rats were fed a liquid diet containing ethanol as 35% of total calories or pair-fed a control diet that isocalorically substituted maltose dextrins for ethanol for 4 wk. Lipolysis was measured by glycerol release over 1 h with or without agonists in adipocytes isolated from epididymal fat. Chronic ethanol feeding decreased beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated lipolysis, but had no effect on basal lipolysis. In response to beta-adrenergic activation, the early peak of cAMP accumulation was suppressed after ethanol feeding, although the basal cAMP concentration in adipocytes did not differ between pair- and ethanol-fed rats. The suppression in cAMP accumulation caused by ethanol feeding was associated with increased activity of phosphodiesterase 4. Chronic ethanol feeding also decreased beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated protein kinase A activation and phosphorylation of its downstream proteins, perilipin A and hormone-sensitive lipase, the primary lipase-mediating lipolysis. In conclusion, these data suggest that chronic ethanol feeding increased phosphodiesterase 4 activity in adipocytes, resulting in decreased accumulation of cAMP in response to beta-adrenergic activation and a suppression of beta-adrenergic stimulation of lipolysis.
Figures

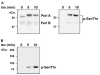
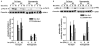

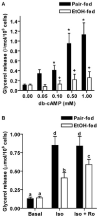
References
-
- Room R, Babor T, Rehm J. Alcohol and public health. Lancet. 2005;365:519–530. - PubMed
-
- Baraona E, Lieber CS. Effects of ethanol on lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1979;20:289–315. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniyan V, Nalini N. The potential beneficial effect of leptin on an experimental model of hyperlipidemia, induced by chronic ethanol treatment. Clin Chim Acta. 2003;337:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Khovidhunkit W, Kim MS, Memon RA, Shigenaga JK, Moser AH, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1169–1196. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura MT, Cheon Y, Li Y, Nara TY. Mechanisms of regulation of gene expression by fatty acids. Lipids. 2004;39:1077–1083. - PubMed

