The influence of age and gender on resting energy expenditure in severely burned children
- PMID: 16794397
- PMCID: PMC1570586
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000217678.78472.d3
The influence of age and gender on resting energy expenditure in severely burned children
Abstract
Introduction: Recent evidence suggests that female severely burned children have higher endogenous anabolic hormone levels and a shorter ICU stay compared with males. The purpose of this study was to analyze the influence of age and gender on resting energy expenditure (REE) in severely burned children from acute hospitalization through 12 months postburn.
Methods: A total of 100 pediatric patients with > 40% total body surface area (TBSA) burn were enrolled in a prospective study and followed by indirect calorimetry measurements. The REE was expressed as actual REE kcal/d, percent of predicted REE, and REE/ body mass index (BMI). Statistical analysis was performed by Student t test and one-way ANOVA for repeated measures. Significance was accepted at P < 0.05.
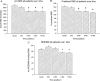
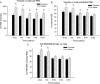
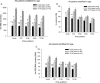
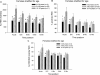
Results: The measured REE was significantly higher in males versus females at all time points (P < 0.05). The percent of predicted REE was significantly higher in males versus females during the acute hospitalization, at discharge, 6 and 9 months postburn (P < 0.05). The REE/BMI showed a significant difference between males and females at the acute and discharge time period (P < 0.05). In children 3 to 9.9 years of age, the measured REE and the percent of predicted REE were significantly higher in males versus females during the acute study, at discharge and 6 months postburn (P < 0.05). The measured REE at discharge, 9 and 12 months postburn for children >10 years of age was significantly higher in males compared with females (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Data show that female children exert a decreased hypermetabolic response compared with male children, which may improve burn outcomes in females.
Figures



References
-
- Seashore JH, Seashore MR. Protein requirements of infants receiving total parental nutrition. J Pediatr Surg. 1976;11:645. - PubMed
-
- Rubecz I, Mestyan P, Varga P, et al. Energy metabolism, substrate utilization, and nitrogen balance in parentally fed postoperative neonates and infants: the effects of glucose, glucose + amino acids, lipid + amino acids infused in isocaloric amounts. J Pediatr. 1981;98:42. - PubMed
-
- Mickell JJ. Urea nitrogen excretion in critically ill children. Pediatrics. 1981;70:949. - PubMed
-
- Milner EA, Cioffi WG, Mason AD, et al. A longitudinal study of resting energy expenditure in thermally injured patients. J Trauma. 1994;37:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Ireton-Jones CS, Turner WW Jr, Baxter CR. The effect of burn wound excision on measured energy expenditure and urinary nitrogen excretion. J Trauma. 1987;27:217–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

