Current-level discrimination in the context of interleaved, multichannel stimulation in cochlear implants: effects of number of stimulated electrodes, pulse rate, and electrode separation
- PMID: 16794913
- PMCID: PMC2430008
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-006-0045-8
Current-level discrimination in the context of interleaved, multichannel stimulation in cochlear implants: effects of number of stimulated electrodes, pulse rate, and electrode separation
Abstract
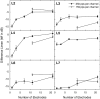
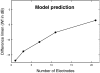
The ability of cochlear implantees to detect an increment in current level at one of many stimulated electrodes was investigated. Such changes in the electric profile provide information for cochlear implantees to discriminate numerous sounds, especially vowels. In Experiment 1, sensitivity to increases in current level at one stimulation site in the electric profile decreased as the number of stimulated electrodes increased. This outcome was most likely a result of decreased stimulus levels at individual electrodes that were required to retain a comfortable loudness when the number of active electrodes was increased. Experiment 2 investigated the effects of pulse rate and separation between stimulation sites when the levels in percent of dynamic range and number of stimulated electrodes were held constant. The effect of pulse rate and electrode separation varied among listeners. The sensitivity of 6 of 9 listeners was best at the pulse rate that they used clinically. This might have been the result of adaptation to the clinical pulse rate, or listeners might have chosen their inherently best pulse rate during the clinical fitting.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparisons between detection threshold and loudness perception for individual cochlear implant channels.Ear Hear. 2014 Nov-Dec;35(6):641-51. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000058. Ear Hear. 2014. PMID: 25036146 Free PMC article.
-
Loudness summation for pulsatile electrical stimulation of the cochlea: effects of rate, electrode separation, level, and mode of stimulation.J Acoust Soc Am. 2001 Sep;110(3 Pt 1):1514-24. doi: 10.1121/1.1394222. J Acoust Soc Am. 2001. PMID: 11572362
-
Rate discrimination at low pulse rates in normal-hearing and cochlear implant listeners: Influence of intracochlear stimulation site.J Acoust Soc Am. 2016 Apr;139(4):1578. doi: 10.1121/1.4944564. J Acoust Soc Am. 2016. PMID: 27106306
-
Loudness growth in cochlear implants: effect of stimulation rate and electrode configuration.Hear Res. 2005 Apr;202(1-2):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2004.10.004. Hear Res. 2005. PMID: 15811699
-
Spectral loudness summation for electrical stimulation in cochlear implant users.Int J Audiol. 2015;54(11):818-27. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2015.1046090. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Int J Audiol. 2015. PMID: 26068301
Cited by
-
A psychophysical method for measuring spatial resolution in cochlear implants.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012 Feb;13(1):145-57. doi: 10.1007/s10162-011-0294-z. Epub 2011 Oct 15. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22002609 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Envelope Interactions in Multi-Channel Amplitude Modulation Frequency Discrimination by Cochlear Implant Users.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 2;10(10):e0139546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139546. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26431043 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of carrier pulse rate and stimulation site on modulation detection by subjects with cochlear implants.J Acoust Soc Am. 2007 Apr;121(4):2236-46. doi: 10.1121/1.2537501. J Acoust Soc Am. 2007. PMID: 17471737 Free PMC article.
-
Current-level discrimination and spectral profile analysis in multi-channel electrical stimulation.J Acoust Soc Am. 2008 Nov;124(5):3142-57. doi: 10.1121/1.2981638. J Acoust Soc Am. 2008. PMID: 19045799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1121/1.1610452', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1610452'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14587605', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14587605/'}]}
- BoËx C, Kos M-I, Pelizzone M. Forward masking in different cochlear implant systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 114:2058–2065, 2003. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1121/1.422777', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1121/1.422777'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9604350', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9604350/'}]}
- Chatterjee M, Shannon RV. Forward masked excitation patterns in multielectrode electrical stimulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103:2565–2572, 1998. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0378-5955(03)00174-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5955(03)00174-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12948604', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12948604/'}]}
- de Balthasar C, BoËx C, Cosendai G, Valentini G, Sigrist A, Plizzone M. Channel interactions with high-rate biphasic electrical stimulation in cochlear implant subjects. Hear. Res. 182:77–87, 2003. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.heares.2004.11.010', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2004.11.010'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15811709', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15811709/'}]}
- Drennan WR, Pfingst BE. Current-level discrimination using bipolar and monopolar electrode configurations in cochlear implants. Hear. Res. 202:170–179, 2005. - PubMed
-
- None
- Green DM. Profile Analysis. Oxford University Press, NY, 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

