Aphid alarm pheromone produced by transgenic plants affects aphid and parasitoid behavior
- PMID: 16798877
- PMCID: PMC1502488
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603998103
Aphid alarm pheromone produced by transgenic plants affects aphid and parasitoid behavior
Abstract
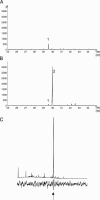
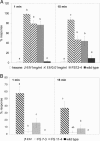
The alarm pheromone for many species of aphids, which causes dispersion in response to attack by predators or parasitoids, consists of the sesquiterpene (E)-beta-farnesene (Ebetaf). We used high levels of expression in Arabidopsis thaliana plants of an Ebetaf synthase gene cloned from Mentha x piperita to cause emission of pure Ebetaf. These plants elicited potent effects on behavior of the aphid Myzus persicae (alarm and repellent responses) and its parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (an arrestant response). Here, we report the transformation of a plant to produce an insect pheromone and demonstrate that the resulting emission affects behavioral responses at two trophic levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


References
-
- Hardie J., Pickett J. A., Pow E. M., Smiley D. W. M. In: Pheromones of Non-Lepidopteran Insects Associated with Agricultural Plants. Hardie J., Minks A. K., editors. Wallingford, U.K.: CAB International; 1999. pp. 227–250.
-
- Kunert G., Otto S., Weisser W. W., Röse U. S. R., Gershenzon J. Ecol. Lett. 2005;8:596–603.
-
- Abassi S. A. L., Birkett M. A., Pettersson J., Pickett J. A., Wadhams L. J., Woodcock C. M. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000;26:1765–1771.
-
- Micha S. G., Wyss U. Chemoecology. 1996;7:132–139.
-
- Du Y. J., Poppy G. M., Powell W., Pickett J. A., Wadhams L. J., Woodcock C. M. J. Chem. Ecol. 1998;24:1355–1368.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

