Transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radiculopathy: preganglionic versus conventional approach
- PMID: 16799275
- PMCID: PMC2667587
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.2.139
Transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radiculopathy: preganglionic versus conventional approach
Abstract
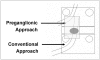
Objective: The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effectiveness of transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) with using a preganglionic approach for treating lumbar radiculopathy when the nerve root compression was located at the level of the supra-adjacent intervertebral disc.
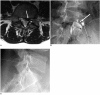
Materials and methods: The medical records of the patients who received conventional TFESI at our department from June 2003 to May 2004 were retrospectively reviewed. TFESI was performed in a total of 13 cases at the level of the exiting nerve root, in which the nerve root compression was at the level of the supra-adjacent intervertebral disc (the conventional TFESI group). Since June 2004, we have performed TFESI with using a preganglionic approach at the level of the supra-adjacent intervertebral disc (for example, at the neural foramen of L4-5 for the L5 nerve root) if the nerve root compression was at the level of the supra-adjacent intervertebral disc. Using the inclusion criteria described above, 20 of these patients were also consecutively enrolled in our study (the preganglionic TFESI group). The treatment outcome was assessed using a 5-point patient satisfaction scale and by using a VAS (visual assessment scale). A successful outcome required a patient satisfaction scale score of 3 (very good) or 4 (excellent), and a reduction on the VAS score of > 50% two weeks after performing TFESI. Logistic regression analysis was also performed.
Results: Of the 13 patients in the conventional TFESI group, nine showed satisfactory improvement two weeks after TFESI (69.2%). However, in the preganglionic TFESI group, 18 of the 20 patients (90%) showed satisfactory improvement. The difference between the two approaches in terms of TFESI effectiveness was of borderline significance (p = 0.056; odds ratio: 10.483).
Conclusion: We conclude that preganglionic TFESI has the better therapeutic effect on radiculopathy caused by nerve root compression at the level of the supra-adjacent disc than does conventional TFESI, and the difference between the two treatments had borderline statistical significance.
Figures
Comment in
-
Epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radiculopathy.Korean J Radiol. 2006 Apr-Jun;7(2):77-9. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.2.77. Korean J Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16799267 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of transforaminal epidural steroid injection by using a preganglionic approach: a prospective randomized controlled study.Radiology. 2007 Nov;245(2):584-90. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2452062007. Radiology. 2007. PMID: 17940309 Clinical Trial.
-
The dosages of corticosteroid in transforaminal epidural steroid injections for lumbar radicular pain due to a herniated disc.Pain Physician. 2011 Jul-Aug;14(4):361-70. Pain Physician. 2011. PMID: 21785479 Clinical Trial.
-
Contrast flow selectivity during transforaminal lumbosacral epidural steroid injections.Pain Physician. 2008 Nov-Dec;11(6):855-61. Pain Physician. 2008. PMID: 19057631
-
Comparison of clinical efficacy of transforaminal and caudal epidural steroid injection in lumbar and lumbosacral disc herniation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Spine J. 2018 Dec;18(12):2343-2353. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.06.720. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 30030083
-
Transforaminal epidural steroid injection in the treatment of lumbosacral radicular pain caused by epidural lipomatosis: a case series and review.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2014;27(2):181-90. doi: 10.3233/BMR-130434. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 24254495 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Safe Triangle Approach Versus Kambin's Triangle Approach: Does Approach Really Matter in Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection (TFESI) for Lumbar Disc Herniation?Cureus. 2023 Nov 12;15(11):e48701. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48701. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38094530 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonography-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Painful Stump Neuromas to Relieve Postamputation Pain: A Pilot Study.J Pain Res. 2020 Dec 18;13:3437-3445. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S283986. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 33376389 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Variations in selective nerve root block technique.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013 Oct;95(7):515-8. doi: 10.1308/003588413X13629960048073. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013. PMID: 24112500 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Epidural Steroid Injection in Management of Lumbar Prolapsed Intervertebral Disc: A Comparison of Caudal, Transforaminal and Interlaminar Routes.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Jul;10(7):RC05-11. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/18208.8127. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27630917 Free PMC article.
-
Kambin's Triangle Approach of Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injection with Spinal Stenosis.Ann Rehabil Med. 2011 Dec;35(6):833-43. doi: 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.833. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011. PMID: 22506212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robecchi A, Capra R. Hydrocortisone (compound F); first clinical experiments in the field of rheumatology. Minerva Med. 1952;43:1259–1163. - PubMed
-
- Benzon HT. Epidural steroid injections for low back pain and lumbosacral radiculopathy. Pain. 1986;24:277–295. - PubMed
-
- Vad VB, Bhat AL, Lutz GE, Cammisa F. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections in lumbosacral radiculopathy: a prospective randomized study. Spine. 2002;27:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Gajraj NM. Selective nerve root blocks for low back pain and radiculopathy. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2004;29:243–256. - PubMed
-
- Sitzman BT. Epidural injections. In: Fenton DS, Czervionke LF, editors. Image-guided spine intervention. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2003. pp. 99–126.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

