Techniques of EMG signal analysis: detection, processing, classification and applications
- PMID: 16799694
- PMCID: PMC1455479
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo115
Techniques of EMG signal analysis: detection, processing, classification and applications
Erratum in
-
Techniques of EMG signal analysis: detection, processing, classification and applications (Correction).Biol Proced Online. 2006;8:163. doi: 10.1251/bpo124. Biol Proced Online. 2006. PMID: 19565309 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Electromyography (EMG) signals can be used for clinical/biomedical applications, Evolvable Hardware Chip (EHW) development, and modern human computer interaction. EMG signals acquired from muscles require advanced methods for detection, decomposition, processing, and classification. The purpose of this paper is to illustrate the various methodologies and algorithms for EMG signal analysis to provide efficient and effective ways of understanding the signal and its nature. We further point up some of the hardware implementations using EMG focusing on applications related to prosthetic hand control, grasp recognition, and human computer interaction. A comparison study is also given to show performance of various EMG signal analysis methods. This paper provides researchers a good understanding of EMG signal and its analysis procedures. This knowledge will help them develop more powerful, flexible, and efficient applications.
Figures
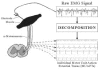
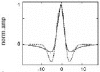

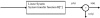
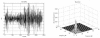

References
-
- Shahid S. Higher Order Statistics Techniques Applied to EMG Signal Analysis and Characterization. Ph.D. thesis, University of Limerick; Ireland, 2004.
-
- Nikias CL, Raghuveer MR. Bispectrum estimation: A digital signal processing framework. IEEE Proceedings on Communications and Radar. 1987;75(7):869–891.
-
- Basmajian JV, de Luca CJ. Muscles Alive - The Functions Revealed by Electromyography. The Williams & Wilkins Company; Baltimore, 1985.
-
- Cram JR, Kasman GS, Holtz J. Introduction to Surface Electromyography. Aspen Publishers Inc.; Gaithersburg, Maryland, 1998.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

