Metabolic engineering of potato tuber carotenoids through tuber-specific silencing of lycopene epsilon cyclase
- PMID: 16800876
- PMCID: PMC1570464
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-6-13
Metabolic engineering of potato tuber carotenoids through tuber-specific silencing of lycopene epsilon cyclase
Abstract
Background: Potato is a major staple food, and modification of its provitamin content is a possible means for alleviating nutritional deficiencies. beta-carotene is the main dietary precursor of vitamin A. Potato tubers contain low levels of carotenoids, composed mainly of the xanthophylls lutein, antheraxanthin, violaxanthin, and of xanthophyll esters. None of these carotenoids have provitamin A activity.
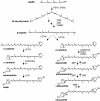
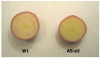
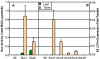
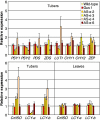
Results: We silenced the first dedicated step in the beta-epsilon- branch of carotenoid biosynthesis, lycopene epsilon cyclase (LCY-e), by introducing, via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, an antisense fragment of this gene under the control of the patatin promoter. Real Time measurements confirmed the tuber-specific silencing of Lcy-e. Antisense tubers showed significant increases in beta-beta-carotenoid levels, with beta-carotene showing the maximum increase (up to 14-fold). Total carotenoids increased up to 2.5-fold. These changes were not accompanied by a decrease in lutein, suggesting that LCY-e is not rate-limiting for lutein accumulation. Tuber-specific changes in expression of several genes in the pathway were observed.
Conclusion: The data suggest that epsilon-cyclization of lycopene is a key regulatory step in potato tuber carotenogenesis. Upon tuber-specific silencing of the corresponding gene, beta-beta-carotenoid and total carotenoid levels are increased, and expression of several other genes in the pathway is modified.
Figures

References
-
- Burkhardt PK, Beyer P, Wunn J, Kloti A, Armstrong GA, Schledz M, von Lintig J, Potrykus I. Transgenic rice (Oryza sativa) endosperm expressing daffodil (Narcissus pseudonarcissus) phytoene synthase accumulates phytoene, a key intermediate of provitamin A biosynthesis. Plant J. 1997;11:1071–1078. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11051071.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

