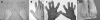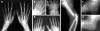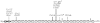A molecular and clinical study of Larsen syndrome caused by mutations in FLNB
- PMID: 16801345
- PMCID: PMC2598053
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.043687
A molecular and clinical study of Larsen syndrome caused by mutations in FLNB
Abstract
Background: Larsen syndrome is an autosomal dominant osteochondrodysplasia characterised by large-joint dislocations and craniofacial anomalies. Recently, Larsen syndrome was shown to be caused by missense mutations or small inframe deletions in FLNB, encoding the cytoskeletal protein filamin B. To further delineate the molecular causes of Larsen syndrome, 20 probands with Larsen syndrome together with their affected relatives were evaluated for mutations in FLNB and their phenotypes studied.
Methods: Probands were screened for mutations in FLNB using a combination of denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography, direct sequencing and restriction endonuclease digestion. Clinical and radiographical features of the patients were evaluated.
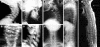
Results and discussion: The clinical signs most frequently associated with a FLNB mutation are the presence of supernumerary carpal and tarsal bones and short, broad, spatulate distal phalanges, particularly of the thumb. All individuals with Larsen syndrome-associated FLNB mutations are heterozygous for either missense or small inframe deletions. Three mutations are recurrent, with one mutation, 5071G-->A, observed in 6 of 20 subjects. The distribution of mutations within the FLNB gene is non-random, with clusters of mutations leading to substitutions in the actin-binding domain and filamin repeats 13-17 being the most common cause of Larsen syndrome. These findings collectively define autosomal dominant Larsen syndrome and demonstrate clustering of causative mutations in FLNB.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Larsen L J, Schottstaedt E R, Bost F C. Multiple congenital dislocations associated with characteristic facial abnormality. J Pediatr 195037(4)574–581. - PubMed
-
- Latta R J, Graham C B, Aase J, Scham S M, Smith D W. Larsen's syndrome: a skeletal dysplasia with multiple joint dislocations and unusual facies. J Pediatr 197178(2)291–298. - PubMed
-
- Silverman F N. [Larsen's syndrome: congenital dislocation of the knees and other joints, distinctive facies, and, frequently, cleft palate]. Ann Radiol (Paris) 197215(3)297–328. - PubMed
-
- Harris R, Cullen C H. Autosomal dominant inheritance in Larsen's syndrome. Clin Genet 19712(2)87–90. - PubMed
-
- Oki T, Terashima Y, Murachi S, Nogami H. Clinical features and treatment of joint dislocations in Larsen's syndrome. Report of three cases in one family. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1976(119)206–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous