Low-level resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 in vitro associated with qacA gene carriage is independent of multidrug efflux pump activity
- PMID: 16801425
- PMCID: PMC1489806
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00028-06
Low-level resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 in vitro associated with qacA gene carriage is independent of multidrug efflux pump activity
Abstract
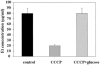
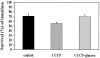
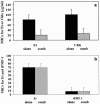
Thrombin-induced platelet microbial protein 1 (tPMP-1), a cationic antimicrobial polypeptide released from thrombin-stimulated rabbit platelets, targets the Staphylococcus aureus cytoplasmic membrane to initiate its microbicidal effects. In vitro resistance to tPMP-1 correlates with survival advantages in vivo. In S. aureus, the plasmid-carried qacA gene encodes a multidrug transporter, conferring resistance to organic cations (e.g., ethidium [Et]) via proton motive force (PMF)-energized export. We previously showed that qacA also confers a tPMP-1-resistant (tPMP-1r) phenotype in vitro. The current study evaluated whether (i) transporters encoded by the qacB and qacC multidrug resistance genes also confer tPMP-1r and (ii) tPMP-1r mediated by qacA is dependent on efflux pump activity. In contrast to tPMP-1r qacA-bearing strains, the parental strain and its isogenic qacB- and qacC-containing strains were tPMP-1 susceptible (tPMP-1s). Efflux pump inhibition by cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone abrogated Etr, but not tPMP-1r, in the qacA-bearing strain. In synergy assays, exposure of the qacA-bearing strain to tPMP-1 did not affect the susceptibility of Et (ruling out Et-tPMP-1 cotransport). The following cytoplasmic membrane parameters did not differ significantly between the qacA-bearing and parental strains: contents of the major phospholipids; asymmetric distributions of the positively charged species, lysyl-phosphotidylglycerol; fatty acid composition; and relative surface charge. Of note, the qacA-bearing strain exhibited greater membrane fluidity than that of the parental, qacB-, or qacC-bearing strain. In conclusion, among these families of efflux pumps, only the multidrug transporter encoded by qacA conferred a tPMP-1r phenotype. These data suggest that qacA-encoded tPMP-1r results from the impact of a specific transporter upon membrane structure or function unrelated to PMF-dependent peptide efflux.
Figures
References
-
- Bayer, A. S., D. Cheng, M. R. Yeaman, G. R. Corey, R. S. McClelland, L. J. Harrel, and V. G. Fowler, Jr. 1998. In vitro resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein among clinical bacteremic isolates of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with an endovascular infectious source. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:3169-3172. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer, A. S., P. McNamara, M. R. Yeaman, N. Lucindo, T. Jones, A. L. Cheung, H.-G. Sahl, and R. A. Proctor. 2006. Transposon disruption of the complex I NADH oxidoreductase gene (snoD) in Staphylococcus aureus is associated with reduced susceptibility to the microbicidal activity of thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1. J. Bacteriol. 188:211-222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer, A. S., R. Prasad, J. Chandra, A. Koul, M. Smriti, A. Varma, R. A. Skurray, N. Firth, M. H. Brown, S.-P. Koo, and M. R. Yeaman. 2000. In vitro resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is associated with alterations in cytoplasmic membrane fluidity. Infect. Immun. 68:3548-3553. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bengoechea, J. A., and M. Skurnik. 2000. Temperature-regulated efflux pump/potassium antiporter system mediates resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Yersinia. Mol. Microbiol. 37:67-80. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. H., and R. A. Skurray. 2001. Staphylococcal multidrug efflux protein QacA. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 3:163-170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

