Intrinsic macrolide resistance of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is inducible
- PMID: 16801446
- PMCID: PMC1489773
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00264-06
Intrinsic macrolide resistance of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is inducible
Abstract
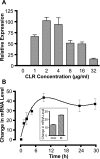
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is intrinsically resistant to macrolides, a characteristic associated with expression of the erm(37) gene. This intrinsic resistance was found to be inducible with clarithromycin and the ketolide HMR3004. Furthermore, underlying the phenotypic induction was an increase in erm(37) mRNA levels.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffner, S. E., L. Gezelius, and B. Olsson-Liljequist. 1997. In-vitro activity of fluorinated quinolones and macrolides against drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 40:885-888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

