Interactions between glycopeptides and beta-lactams against isogenic pairs of teicoplanin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Staphylococcus haemolyticus
- PMID: 16801450
- PMCID: PMC1489795
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00260-06
Interactions between glycopeptides and beta-lactams against isogenic pairs of teicoplanin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Abstract
Four isogenic derivatives with stably increased glycopeptide MICs (all become resistant to teicoplanin) were obtained from four glycopeptide-susceptible clinical isolates of Staphylococcus haemolyticus. All strains were extensively analyzed and compared for a number of distinctive features. In particular, the results provided insights into the puzzling issue of antistaphylococcal interactions between glycopeptides and beta-lactams, especially the paradox of double zones around beta-lactam disks and the relationships between autolysis rate and type of interaction.
Figures
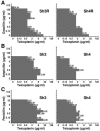

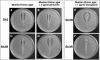

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of spontaneous resistance to glycopeptide antibiotics in staphylococcal populations.J Chemother. 1989 Jul;1(4 Suppl):389-90. J Chemother. 1989. PMID: 16312453 No abstract available.
-
Epidemiological and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus haemolyticus strains, from a hematology ward, with decreased susceptibility to glycopeptides.Can J Microbiol. 2011 Jun;57(6):476-84. doi: 10.1139/w11-033. Epub 2011 May 31. Can J Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21627487
-
In-vitro study of the synergy between beta-lactam antibiotics and glycopeptides against enterococci.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997 Apr;39(4):461-70. doi: 10.1093/jac/39.4.461. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997. PMID: 9145818
-
Glycopeptide resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000 Jun;19(6):403-17. doi: 10.1007/s100960000299. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10947214 Review.
-
Microbiological properties of teicoplanin.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 Suppl A:1-13. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988. PMID: 2965119 Review.
Cited by
-
Striking "seesaw effect" between daptomycin nonsusceptibility and beta-lactam susceptibility in Staphylococcus haemolyticus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 May;55(5):2495-6; author reply 296-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00224-11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21527800 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Characterization of gut bacterial flora of Apis mellifera from north-west Pakistan.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Feb;25(2):388-392. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.05.008. Epub 2017 May 18. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29472796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman, T. L. 2003. Staphylococcus, Micrococcus, and other catalase-positive cocci that grow aerobically, p. 384-404. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, J. H. Jorgensen, M. A. Pfaller, and R. H. Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 8th ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Barr, J. G., E. T. Smyth, and G. M. Hogg. 1990. In vitro antimicrobial activity of imipenem in combination with vancomycin or teicoplanin against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9:804-809. - PubMed
-
- Biavasco, F., E. Giovanetti, M. P. Montanari, R. Lupidi, and P. E. Varaldo. 1991. Development of in-vitro resistance to glycopeptide antibiotics: assessment in staphylococci of different species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 27:71-79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

