In situ localization of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in human and rat brain
- PMID: 16801529
- PMCID: PMC3957801
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.5A6870.2006
In situ localization of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in human and rat brain
Abstract
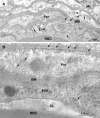
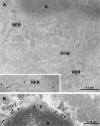
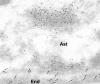
Transport of several xenobiotics including pharmacological agents into or out of the central nervous system (CNS) involves the expression of ATP-dependent, membrane-bound efflux transport proteins such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp) at the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Previous studies have documented gene and protein expression of P-gp in brain microvessel endothelial cells. However, the exact localization of P-gp, particularly at the abluminal side of the BBB, remains controversial. In the present study we examined the cellular/subcellular distribution of P-gp in situ in rat and human brain tissues using immunogold cytochemistry at the electron microscope level. P-gp localizes to both the luminal and abluminal membranes of capillary endothelial cells as well as to adjacent pericytes and astrocytes. Subcellularly, P-gp is distributed along the nuclear envelope, in caveolae, cytoplasmic vesicles, Golgi complex, and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). These results provide evidence for the expression of P-gp in human and rodent brain capillary along their plasma membranes as well as at sites of protein synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane trafficking. In addition, its presence at the luminal and abluminal poles of the BBB, including pericytes and astrocyte plasma membranes, suggests that this glycoprotein may regulate drug transport processes in the entire CNS BBB at both the cellular and subcellular level.
Figures

References
-
- Ballerini P, Di Iorio P, Ciccarelli R, Nargi E, D'Alimonte I, Traversa U, Rathbone MP, et al. (2002) Glial cells express multiple ATP binding cassette proteins which are involved in ATP release. Neuroreport 13:1789–1792 - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. (2004) Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol 66:413–419 - PubMed
-
- Bendayan M. (1995) Colloidal gold post-embedding immunocytochemistry. Prog Histochem Cytochem 29:1–159 - PubMed
-
- Bendayan R, Lee G, Bendayan M. (2002) Functional expression and localization of P-glycoprotein at the blood brain barrier. Microsc Res Tech 57:365–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

