Relative efficacy of drugs for the treatment of sleepiness in narcolepsy
- PMID: 1680245
- PMCID: PMC2246380
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/14.3.218
Relative efficacy of drugs for the treatment of sleepiness in narcolepsy
Abstract
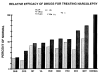
A survey was conducted on 10 polysomnographic studies on the pharmacologic treatment of the sleepiness of narcolepsy. Three studies employed the MSLT and 7 employed the MWT as their polygraphic measure of sleep tendency. Statistically and clinically significant therapeutic changes were apparent for pemoline, modafinil, dextroamphetamine and methylphenidate. Codeine, ritanserin and protriptyline did show statistically significant effects. The common feature among the drugs that did produce clinically significant improvements seems to be facilitatory action on central catecholaminergic transmission. Within this group of drugs, only methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine brought MWT sleep latencies to approximately 70% of normal levels.
Figures
References
-
- Fry JM, Pressman MR, DiPhillipo MA, Forst-Paulus M. Treatment of narcolepsy with codeine. Sleep. 1986;9:269–74. - PubMed
-
- Scrima L, Johnson FH, Thomas EE, Hiller FC. Effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) on multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) in narcolepsy patients: a long term study. Sleep Res. 1990;19:288. - PubMed
-
- Scrima L, Hartman PG, Johnson FH, Thomas EE, Hiller FC. Effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) on sleep of narcolepsy patients: a double-blind study. Sleep. 1990;13(6):479. - PubMed
-
- Lammers GJ, Arends J, Declerck AC, Kamphuisen HAC, Schouwink G, Troost J. Ritanserin, a serotonin 5-HT2 antagonist, reduces daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy (abstract). 10th Congress of The European Sleep Research Society; Strasbourg. 1990. p. 258.
-
- Godbout R, Poirier G, Montplaisir J. New treatments for narcolepsy (viloxazine). Narcolepsy 3rd International Symposium; San Diego. June 1988; pp. 79–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

