Identification of the lipopolysaccharide modifications controlled by the Salmonella PmrA/PmrB system mediating resistance to Fe(III) and Al(III)
- PMID: 16803591
- PMCID: PMC1618816
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05273.x
Identification of the lipopolysaccharide modifications controlled by the Salmonella PmrA/PmrB system mediating resistance to Fe(III) and Al(III)
Abstract
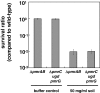
Iron is an essential metal but can be toxic in excess. While several homeostatic mechanisms prevent oxygen-dependent killing promoted by Fe(II), little is known about how cells cope with Fe(III), which kills by oxygen-independent means. Several Gram-negative bacterial species harbour a regulatory system - termed PmrA/PmrB - that is activated by and required for resistance to Fe(III). We now report the identification of the PmrA-regulated determinants mediating resistance to Fe(III) and Al(III) in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. We establish that these determinants remodel two regions of the lipopolysaccharide, decreasing the negative charge of this major constituent of the outer membrane. Remodelling entails the covalent modification of the two phosphates in the lipid A region with phosphoethanolamine and 4-aminoarabinose, which has been previously implicated in resistance to polymyxin B, as well as dephosphorylation of the Hep(II) phosphate in the core region by the PmrG protein. A mutant lacking the PmrA-regulated Fe(III) resistance genes bound more Fe(III) than the wild-type strain and was defective for survival in soil, suggesting that these PmrA-regulated lipopolysaccharide modifications aid Salmonella's survival and spread in non-host environments.
Figures


References
-
- Bolivar F, Rodriguez RL, Greene PJ, Betlach MC, Heyneker HL, Boyer HW. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Braun V. Avoidance of iron toxicity through regulation of bacterial iron transport. Biol Chem. 1997;378:779–786. - PubMed
-
- Breazeale SD, Ribeiro AA, Raetz CR. Origin of lipid A species modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose in polymyxin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. An aminotransferase (ArnB) that generates UDP-4-deoxyl-L-arabinose. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:24731–24739. - PubMed
-
- Bruins MR, Kapil S, Oehme FW. Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2000;45:198–207. - PubMed
-
- Chamnongpol S, Dodson W, Cromie MJ, Harris ZL, Groisman EA. Fe(III)-mediated cellular toxicity. Mol Microbiol. 2002;45:711–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

