Sustained renal interstitial macrophage infiltration following chronic angiotensin II infusions
- PMID: 16804106
- PMCID: PMC2001287
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00059.2006
Sustained renal interstitial macrophage infiltration following chronic angiotensin II infusions
Abstract
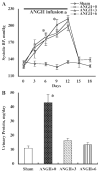
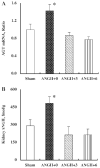
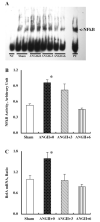
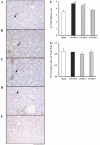
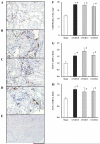
Chronic angiotensin (ANG) II infusions into rats lead to augmented intrarenal levels of ANG II and inflammatory factors, impaired renal function, and progressive hypertension. Residual effects persist after cessation of ANG II infusions, as manifested by a hypertensive response to high-salt intake. This study was performed to determine the residual cytokines and chemokines following the cessation of ANG II infusion. Male Sprague-Dawley rats, maintained on a normal diet, received either a sham operation or continuous ANG II infusion (120 ng/min) subcutaneously via minipumps. The ANG II-infused rats were further subdivided into three subgroups. Minipumps were removed on day 12 with subsequent harvesting of kidneys at 0, 3, and 6 days after cessation of ANG II infusion. After 12 days of ANG II infusion, systolic blood pressure, interstitial fibrosis, preglomerular hypertrophy, and interstitial macrophage infiltration were significantly enhanced compared with the shams. By 3 days following the cessation of ANG II infusion, systolic blood pressure was normalized; however, interstitial fibrosis and preglomerular hypertrophy were still present. Furthermore, increased interstitial macrophage infiltration was still present 6 days after cessation of ANG II infusion. Importantly, augmented mRNA levels of monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 (1.55 +/- 0.15 vs. 1.00 +/- 0.13, relative ratio) and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta(1) (1.52 +/- 0.16 vs. 1.00 +/- 0.08) persisted 6 days after the withdrawal of ANG II infusion (1.60 +/- 0.20 for MCP-1 and 1.43 +/- 0.17 for TGF-beta(1)). Thus, the ANG II-induced activation of MCP-1 and TGF-beta(1) is sustained and may account for the persistent effect of chronic ANG II infusions on interstitial macrophage infiltration, suggesting a possible mechanism for the development of salt sensitivity in ANG II-dependent hypertension.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez V, Quiroz Y, Nava M, Pons H, Rodriguez-Iturbe B. Overload proteinuria is followed by salt-sensitive hypertension caused by renal infiltration of immune cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;283:F1132–F1141. - PubMed
-
- Arthur MJ. Fibrogenesis II. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G245–G249. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson JJ, Senior RM. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28:12–24. - PubMed
-
- Border WA, Noble N. Maximizing hemodynamic-independent effects of angiotensin II antagonists in fibrotic diseases. Semin Nephrol. 2001;21:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Border WA, Noble NA. TGF-beta in kidney fibrosis: a target for gene therapy. Kidney Int. 1997;51:1388–1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

