Prognostic value of cell cycle regulatory proteins in muscle-infiltrating bladder cancer
- PMID: 16804724
- PMCID: PMC12161030
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-006-0123-7
Prognostic value of cell cycle regulatory proteins in muscle-infiltrating bladder cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The aims of this study were to investigate the expression levels of proteins involved in cell cycle regulation in specimens of bladder cancer and to correlate them with the clinicopathological characteristics, proliferative activity and survival.
Methods: Eighty-two specimens obtained from patients affected by muscle-invasive bladder cancer were evaluated immunohistochemically for p53, p21 and cyclin D1 expression, as well as for the tumour proliferation index, Ki-67. The statistical analysis included Kaplan-Meier curves with log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards models.
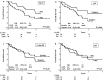
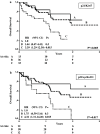
Results: In univariate analyses, low Ki-67 proliferation index (P = 0.045) and negative p21 immunoreactivity (P = 0.04) were associated to patient's overall survival (OS), but in multivariate models p21 did not reach statistical significance. When the combinations of the variables were assessed in two separate multivariate models that included tumour stage, grading, lymph node status, vascular invasion and perineural invasion, the combined variables p21/Ki-67 or p21/cyclin D1 expression were independent predictors for OS; in particular, patients with positive p21/high Ki-67 (P = 0.015) or positive p21/negative cyclin D1 (P = 0.04) showed the worst survival outcome.
Conclusions: Important alterations in the cell cycle regulatory pathways occur in muscle-invasive bladder cancer and the combined use of cell cycle regulators appears to provide significant prognostic information that could be used to select the patients most suitable for multimodal therapeutic approaches.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Expression of cell-cycle regulatory proteins in endometrial carcinomas: correlations with hormone receptor status and clinicopathologic parameters.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001 Sep;127(9):537-44. doi: 10.1007/s004320100256. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11570574 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of cell cycle markers p53, MDM2, p21, and Ki-67 in superficial bladder tumor recurrence.Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Dec;5(12):4079-84. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10632343
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of cell-cycle regulation biomarkers in bladder cancer.Semin Oncol. 2012 Oct;39(5):524-33. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2012.08.008. Semin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23040249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prognostic Value of Cell Cycle Gene Expression Signatures in Muscle Invasive, High-Grade Bladder Cancer.Bladder Cancer. 2015 Apr 30;1(1):45-63. doi: 10.3233/BLC-150012. Bladder Cancer. 2015. PMID: 30561442 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of Ki-67 Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 13;11(7):e0158891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158891. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27410033 Free PMC article.
-
High Ki-67 Immunohistochemical Reactivity Correlates With Poor Prognosis in Bladder Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis with 13,053 Patients Involved.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(15):e3337. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003337. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27082587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of cyclin D1 overexpression on the prognosis of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2014 Mar 6;12:55. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-55. World J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24602161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc Ser B 34:187–220
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

