Synaptic plasticity: one STEP at a time
- PMID: 16806510
- PMCID: PMC1630769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.06.007
Synaptic plasticity: one STEP at a time
Abstract
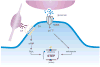
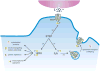
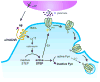
Striatal enriched tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) has recently been identified as a crucial player in the regulation of synaptic function. It is restricted to neurons within the CNS and acts by downregulating the activity of MAP kinases, the tyrosine kinase Fyn and NMDA receptors. By modulating these substrates, STEP acts on several parallel pathways that impact upon the progression of synaptic plasticity. Here, we review recent advances that demonstrate the importance of STEP in normal cognitive function, and its possible involvement in cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
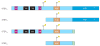
References
-
- Soderling TR, Derkach VA. Postsynaptic protein phosphorylation and LTP. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Salter MW, Kalia LV. Src kinases: a hub for NMDA receptor regulation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Sweatt JD. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14:311–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

