Induction of lactoferrin gene expression in myeloid or mammary gland cells by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax: implications for milk-borne transmission of HTLV-1
- PMID: 16809317
- PMCID: PMC1489047
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00409-06
Induction of lactoferrin gene expression in myeloid or mammary gland cells by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax: implications for milk-borne transmission of HTLV-1
Abstract
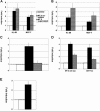
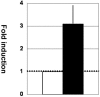
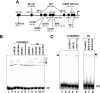
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), the causative agent of adult T-cell leukemia, is transmitted vertically via breastfeeding. We have previously demonstrated that lactoferrin, a major milk protein, enhances HTLV-1 replication, at least in part by upregulating the HTLV-1 long terminal repeat promoter. We now report that HTLV-1 infection can induce lactoferrin gene expression. Coculture with HTLV-1-infected MT-2 cells increased the levels of lactoferrin mRNA in myeloid-differentiated HL-60 cells, as well as MCF-7 cells, models of two probable sources (neutrophils and mammary epithelium) of lactoferrin in breast milk. MT-2 cell coculture could be replaced with cell-free culture supernatants of MT-2 cells to exert the same effect. Furthermore, extracellularly administered Tax protein also induced lactoferrin gene expression at physiologically relevant concentrations. In transient-expression assays, Tax transactivated the lactoferrin gene promoter in HL-60 or MCF-7 cells. Experiments with Tax mutants, as well as site-directed mutants of the lactoferrin promoter reporters, indicated that the NF-kappaB transactivation pathway is critical for Tax induction of the lactoferrin gene promoter activity in myeloid-differentiated HL-60 cells, but not in MCF-7 cells. These results suggest that HTLV-1 infection may be able to induce expression of lactoferrin in a paracrine manner in the lactic compartment. Our findings, in conjunction with our previous study, implicate that mutual interaction between HTLV-1 and lactoferrin would benefit milk-borne transmission of this virus.
Figures
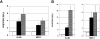
Similar articles
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax activates transcription of the human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene through two nuclear factor-kappaB sites.Cancer Res. 2000 Sep 1;60(17):4939-45. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10987310
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type-I oncoprotein Tax inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis by inducing cellular FLIP through activation of NF-kappaB.Genes Cells. 2006 Feb;11(2):177-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2006.00927.x. Genes Cells. 2006. PMID: 16436054
-
Activation of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 LTR promoter and cellular promoter elements by T cell receptor signaling and HTLV-1 Tax expression.Virology. 2005 Aug 15;339(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.05.015. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15964046
-
Mechanisms of persistent NF-kappaB activation by HTLV-I tax.IUBMB Life. 2005 Feb;57(2):83-91. doi: 10.1080/15216540500078715. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16036567 Review.
-
NF-kappaB in pathogenesis and treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.Int Rev Immunol. 2007 Sep-Dec;26(5-6):269-81. doi: 10.1080/08830180701703364. Int Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18027201 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of lactoferrin gene expression by innate immune stimuli in mouse mammary epithelial HC-11 cells.Biochimie. 2009 Jan;91(1):58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.04.014. Epub 2008 May 15. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 18534195 Free PMC article.
-
Mother-to-Child Transmission of Arboviruses during Breastfeeding: From Epidemiology to Cellular Mechanisms.Viruses. 2021 Jul 7;13(7):1312. doi: 10.3390/v13071312. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular determinants of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 transmission and spread.Viruses. 2011 Jul;3(7):1131-65. doi: 10.3390/v3071131. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mother-to-Child Transmission of HTLV-1 Epidemiological Aspects, Mechanisms and Determinants of Mother-to-Child Transmission.Viruses. 2016 Feb 3;8(2):40. doi: 10.3390/v8020040. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26848683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mother-to-Child Transmission of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1: Mechanisms and Nutritional Strategies for Prevention.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 14;13(16):4100. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164100. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439253 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alefantis, T., K. Mostoller, P. Jain, E. Harhaj, C. Grant, and B. Wigdahl. 2005. Secretion of the human T cell leukemia virus type I transactivator protein Tax. J. Biol. Chem. 280:17353-17362. - PubMed
-
- Aono, H., K. Fujisawa, T. Hasunuma, S. J. Marriott, and K. Nishioka. 1998. Extracellular human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein stimulates the proliferation of human synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 41:1995-2003. - PubMed
-
- Beck, Z., A. Bácsi, X. Liu, P. Ebbesen, I. Andirkó, E. Csoma, J. Kónya, E. Nagy, and F. D. Tóth. 2003. Differential patterns of human cytomegalovirus gene expression in various T-cell lines carrying human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus type I: role of Tax-activated cellular transcription factors. J. Med. Virol. 71:94-104. - PubMed
-
- Brady, J. N. 1992. Extracellular Tax1 protein stimulates NF-κB and expression of NF-κB-responsive Ig kappa and TNF beta genes in lymphoid cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 8:724-727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

