Hepatitis C virus triggers mitochondrial permeability transition with production of reactive oxygen species, leading to DNA damage and STAT3 activation
- PMID: 16809325
- PMCID: PMC1489016
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00321-06
Hepatitis C virus triggers mitochondrial permeability transition with production of reactive oxygen species, leading to DNA damage and STAT3 activation
Abstract
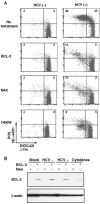
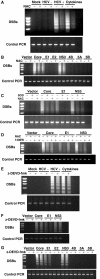
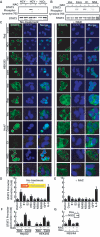
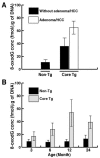
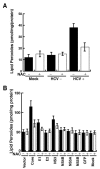
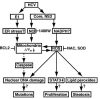
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is frequently associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinomas and non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphomas. Previously, we reported that HCV infection causes cellular DNA damage and mutations, which are mediated by nitric oxide (NO). NO often damages mitochondria, leading to induction of double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs) and accumulation of oxidative DNA damage. Here we report that HCV infection causes production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lowering of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (DeltaPsi(m)) in in vitro HCV-infected cell cultures. The changes in membrane potential could be inhibited by BCL-2. Furthermore, an inhibitor of ROS production, antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), or an inhibitor of NO, 1,400W, prevented the alterations of DeltaPsi(m). The HCV-induced DSB was also abolished by a combination of NO and ROS inhibitors. These results indicated that the mitochondrial damage and DSBs in HCV-infected cells were mediated by both NO and ROS. Among the HCV proteins, core, E1, and NS3 are potent ROS inducers: their expression led to DNA damage and activation of STAT3. Correspondingly, core-protein-transgenic mice showed elevated levels of lipid peroxidation and oxidatively damaged DNA. These HCV studies thus identified ROS, along with the previously identified NO, as the primary inducers of DSBs and mitochondrial damage in HCV-infected cells.
Figures

References
-
- Benali-Furet, N. L., M. Chami, L. Houel, F. De Giorgi, F. Vernejoul, D. Lagorce, L. Buscail, R. Bartenschlager, F. Ichas, R. Rizzuto, and P. Paterlini-Brechot. 2005. Hepatitis C virus core triggers apoptosis in liver cells by inducing ER stress and ER calcium depletion. Oncogene 24:4921-4933. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg, J. F., M. H. Wrzeszczynska, G. Devgan, Y. Zhao, R. G. Pestell, C. Albanese, and J. E. Darnell, Jr. 1999. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98:295-303. - PubMed
-
- Brown, G. C. 2001. Regulation of mitochondrial respiration by nitric oxide inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1504:46-57. - PubMed
-
- Bureau, C., J. Bernad, N. Chaouche, C. Orfila, M. Beraud, C. Gonindard, L. Alric, J. P. Vinel, and B. Pipy. 2001. Nonstructural 3 protein of hepatitis C virus triggers an oxidative burst in human monocytes via activation of NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:23077-23083. - PubMed
-
- Butel, J. S. 2000. Viral carcinogenesis: revelation of molecular mechanisms and etiology of human disease. Carcinogenesis 21:405-426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

