Evolutionary history of the closely related group 2 coronaviruses: porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus, bovine coronavirus, and human coronavirus OC43
- PMID: 16809333
- PMCID: PMC1489060
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02675-05
Evolutionary history of the closely related group 2 coronaviruses: porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus, bovine coronavirus, and human coronavirus OC43
Abstract
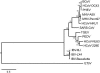
The close genetic and antigenic relatedness among the group 2 coronaviruses human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43), bovine coronavirus (BCoV), and porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (PHEV) suggests that these three viruses with different host specificities diverged fairly recently. In this study, we determined the complete genomic sequence of PHEV (strain PHEV-VW572), revealing the presence of a truncated group 2-specific ns2 gene in PHEV in comparison to other group 2 coronaviruses. Using a relaxed molecular clock approach, we reconstructed the evolutionary relationships between PHEV, BCoV, and HCoV-OC43 in real-time units, which indicated relatively recent common ancestors for these species-specific coronaviruses.
Figures
References
-
- Andries, K., and M. B. Pensaert. 1980. Immunofluorescence studies on the pathogenesis of hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus infection in pigs after oronasal inoculation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 41:1372-1378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

