Orphan care in Botswana's working households: growing responsibilities in the absence of adequate support
- PMID: 16809585
- PMCID: PMC1522103
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2005.072280
Orphan care in Botswana's working households: growing responsibilities in the absence of adequate support
Abstract
Objectives: Botswana has one of the world's highest HIV-prevalence rates and the world's highest percentages of orphaned children among its population. We assessed the ability of income-earning households in Botswana to adequately care for orphans.
Methods: We used data from the Botswana Family Health Needs Study (2002), a sample of 1033 working adults with caregiving responsibilities who used public services, to assess whether households with orphan-care responsibilities encountered financial and other difficulties. Thirty-seven percent of respondents provided orphan care, usually to extended family members. We applied logistic regression models to determine the factors associated with experiencing problems related to orphan caregiving.
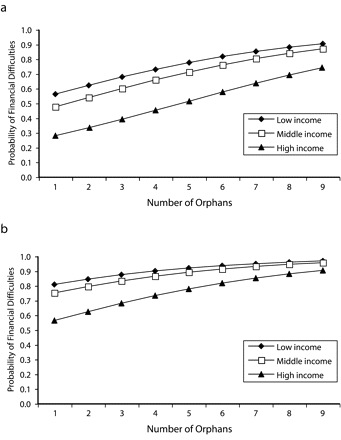
Results: Nearly half of working households with orphan-care responsibilities reported experiencing financial and other difficulties because of orphan care. Issues of concern included caring for multiple orphans, caring for sick adults and orphans simultaneously, receiving no assistance, and low income.
Conclusions: The orphan crisis is impoverishing even working households, where caregivers lack sufficient resources to provide basic needs. Neither the public sector nor communities provide adequate safety nets. International assistance is critical to build capacity within the social welfare infrastructure and to fund community-level activities that support households. Lessons from Botswana's orphan crisis can provide valuable insights to policymakers throughout sub-Saharan Africa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extended family caring for children orphaned by AIDS: balancing essential work and caregiving in a high HIV prevalence nations.AIDS Care. 2007 Mar;19(3):337-45. doi: 10.1080/09540120600763225. AIDS Care. 2007. PMID: 17453567
-
Barriers and incentives to orphan care in a time of AIDS and economic crisis: a cross-sectional survey of caregivers in rural Zimbabwe.BMC Public Health. 2006 Feb 9;6:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-6-27. BMC Public Health. 2006. PMID: 16469104 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging health disparities in Botswana: examining the situation of orphans during the AIDS epidemic.Soc Sci Med. 2007 Jun;64(12):2476-86. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.03.002. Epub 2007 Apr 17. Soc Sci Med. 2007. PMID: 17442471
-
HIV/AIDS, declining family resources and the community safety net.AIDS Care. 2009;21 Suppl 1:34-42. doi: 10.1080/09540120902927593. AIDS Care. 2009. PMID: 22380977 Review.
-
Federal and state efforts to improve care for infants and toddlers.Future Child. 2001 Spring-Summer;11(1):78-97. Future Child. 2001. PMID: 11712458 Review.
Cited by
-
A developmental psychopathology framework of the psychosocial needs of children orphaned by HIV.J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2008 Mar-Apr;19(2):147-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2007.08.004. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2008. PMID: 18328965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
'Older women', customary obligations and orphan foster caregiving: the case of queen mothers in Manya Klo, Ghana.J Cross Cult Gerontol. 2014 Jun;29(2):211-29. doi: 10.1007/s10823-014-9232-y. J Cross Cult Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 24737050
-
Caring for AIDS-orphaned children: an exploratory study of challenges faced by carers in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2010 Dec 1;5(4):344-352. doi: 10.1080/17450128.2010.516372. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2010. PMID: 21165153 Free PMC article.
-
Gogo care and protection of vulnerable children in rural Malawi: changing responsibilities, capacity to provide, and implications for well-being in the era of HIV and AIDS.J Cross Cult Gerontol. 2012 Dec;27(4):335-55. doi: 10.1007/s10823-012-9174-1. J Cross Cult Gerontol. 2012. PMID: 22869344 Clinical Trial.
-
The extent of community and public support available to families caring for orphans in Malawi.AIDS Care. 2009 Apr;21(4):439-47. doi: 10.1080/09540120802298152. AIDS Care. 2009. PMID: 18846456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, United Nations Children’s Fund, US Agency for International Development. Children on the Brink 2004: A Joint Report of New Orphan Estimates and a Framework for Action. New York, NY: United Nations Children’s Fund; 2004.
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, World Health Organization, United Nations Children’s Fund. Epidemiological Fact Sheets on HIV/AIDS and Sexually Transmitted Infections: 2004 Update Botswana. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- MacFarlan M, Sgheri S. The Macroeconomic Impact of HIV/AIDS in Botswana. Working paper 01/80. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund; 2001.
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, World Health Organization, United Nations Children’s Fund. Epidemiological Fact Sheets on HIV/AIDS and Sexually Transmitted Infections: 2002 Update Botswana. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2002.
-
- Botswana 2003 Second Generation HIV/AIDS Surveillance. Gaborone, Botswana: The National AIDS Coordinating Agency; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

