B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and other B cells can produce granzyme B and gain cytotoxic potential after interleukin-21-based activation
- PMID: 16809616
- PMCID: PMC1895576
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-014001
B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and other B cells can produce granzyme B and gain cytotoxic potential after interleukin-21-based activation
Abstract
B cells currently are not viewed as being capable of producing granzyme B or being cytotoxic. We found that B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells treated with interleukin-21 (IL-21) produce low levels of granzyme B. The addition of either CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) or anti-B-cell-receptor antibody (anti-BCR) to IL-21 results in enhanced production of functional granzyme B by B-CLL cells. B-CLL cells treated with IL-21 and CpG ODN undergo apoptosis and are able to induce apoptosis of untreated bystander B-CLL cells. This effect can be inhibited by anti-granzyme B antibody. Benign human B cells, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed lymphoblasts, and many standard lymphoma cell lines produce high levels of granzyme B in response to IL-21 and anti-BCR. Our results suggest that the ability to induce production of functional granzyme B by B cells could open new approaches to the therapy of B-CLL and other B-cell malignancies. Our findings also have significant implications for our understanding of the role of B cells for immune regulation and for a variety of immune phenomena, including cancer immunity, autoimmunity, and infectious immunity.
Figures
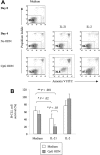



 ) or with IL-21 (▪) was flow cytometrically detected using annexin V, anti-CD19, and PI staining. Averages from 3 independent experiments are shown. Error bars indicate SEM.
) or with IL-21 (▪) was flow cytometrically detected using annexin V, anti-CD19, and PI staining. Averages from 3 independent experiments are shown. Error bars indicate SEM.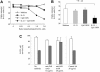
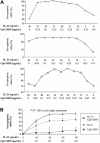
 )ora control antibody (□). B-CLL cell survival was determined by FACS analysis using annexin V/PI staining and counterstaining with antibodies to CD19. Plotted are the mean B-CLL cell-survival rates in percent from 1 representative experiment of 3 with similar results. Error bars indicate SD.
)ora control antibody (□). B-CLL cell survival was determined by FACS analysis using annexin V/PI staining and counterstaining with antibodies to CD19. Plotted are the mean B-CLL cell-survival rates in percent from 1 representative experiment of 3 with similar results. Error bars indicate SD.
References
-
- Bossi G, Trambas C, Booth S, Clark R, Stinchcombe J, Griffiths GM. The secretory synapse: the secrets of a serial killer. Immunol Rev. 2002; 189: 152-160. - PubMed
-
- Wowk ME, Trapani JA. Cytotoxic activity of the lymphocyte toxin granzyme B. Microbes Infect. 2004;6: 752-758. - PubMed
-
- Trapani JA, Sutton VR. Granzyme B: proapoptotic, antiviral and antitumor functions. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15: 533-543. - PubMed
-
- Lord SJ, Rajotte RV, Korbutt GS, Bleackley RC. Granzyme B: a natural born killer. Immunol Rev. 2003;193: 31-38. - PubMed
-
- Froelich CJ, Orth K, Turbov J, et al. New paradigm for lymphocyte granule-mediated cytotoxicity: target cells bind and internalize granzyme B, but an endosomolytic agent is necessary for cytosolic delivery and subsequent apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271: 29073-29079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

