Development of a macrophage-based nanoparticle platform for antiretroviral drug delivery
- PMID: 16809617
- PMCID: PMC1895582
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-012534
Development of a macrophage-based nanoparticle platform for antiretroviral drug delivery
Erratum in
- Blood. 2007 Mar 1;109(5):1816
Abstract
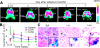
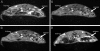
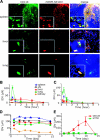
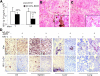
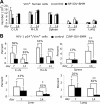
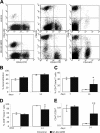
Complex dosing regimens, costs, side effects, biodistribution limitations, and variable drug pharmacokinetic patterns have affected the long-term efficacy of antiretroviral medicines. To address these problems, a nanoparticle indinavir (NP-IDV) formulation packaged into carrier bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) was developed. Drug distribution and disease outcomes were assessed in immune-competent and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected humanized immune-deficient mice, respectively. In the former, NP-IDV formulation contained within BMMs was adoptively transferred. After a single administration, single-photon emission computed tomography, histology, and reverse-phase-high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) demonstrated robust lung, liver, and spleen BMMs and drug distribution. Tissue and sera IDV levels were greater than or equal to 50 microM for 2 weeks. NP-IDV-BMMs administered to HIV-1-challenged humanized mice revealed reduced numbers of virus-infected cells in plasma, lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and lung, as well as, CD4(+) T-cell protection. We conclude that a single dose of NP-IDV, using BMMs as a carrier, is effective and warrants consideration for human testing.
Figures

References
-
- Dam Nielsen S, Kjaer Ersboll A, Mathiesen L, Nielsen JO, Hansen JE. Highly active antiretroviral therapy normalizes the function of progenitor cells in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis. 1998;178: 1299-1305. - PubMed
-
- Pezzotti P, Napoli PA, Acciai S, et al. Increasing survival time after AIDS in Italy: the role of new combination antiretroviral therapies: Tuscany AIDS Study Group. Aids. 1999;13: 249-255. - PubMed
-
- Sharland M, Watkins AM, Dalgleish AG, Cammack N, Westby M. Immune reconstitution in HAART-treated children with AIDS: Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy. Lancet. 1998;352: 577-578. - PubMed
-
- Piot P, Bartos M, Ghys PD, Walker N, Schwartlander B. The global impact of HIV/AIDS. Nature. 2001;410: 968-973. - PubMed
-
- Anabwani G, Navario P. Nutrition and HIV/AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa: an overview. Nutrition. 2005;21: 96-99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2R37 NS 36126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS043985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR 15635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS031492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 MH 64570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01 NS 034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS 31492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 MH064570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS036126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS 43985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

