5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is induced by low-oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions found in solid-tumor microenvironments
- PMID: 16809770
- PMCID: PMC1592699
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00166-06
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is induced by low-oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions found in solid-tumor microenvironments
Abstract
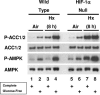
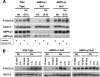
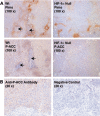
Low oxygen gradients (hypoxia and anoxia) are important determinants of pathological conditions under which the tissue blood supply is deficient or defective, such as in solid tumors. We have been investigating the relationship between the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), the primary transcriptional regulator of the mammalian response to hypoxia, and 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), another regulatory system important for controlling cellular energy metabolism. In the present study, we used mouse embryo fibroblasts nullizygous for HIF-1alpha or AMPK expression to show that AMPK is rapidly activated in vitro by both physiological and pathophysiological low-oxygen conditions, independently of HIF-1 activity. These findings imply that HIF-1 and AMPK are components of a concerted cellular response to maintain energy homeostasis in low-oxygen or ischemic-tissue microenvironments. Finally, we used transformed derivatives of wild-type and HIF-1alpha- or AMPKalpha-null mouse embryo fibroblasts to determine whether AMPK is activated in vivo. We obtained evidence that AMPK is activated in authentic hypoxic tumor microenvironments and that this activity overlaps with regions of hypoxia detected by a chemical probe. We also showed that AMPK is important for the growth of this tumor model.
Figures
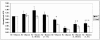
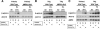


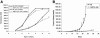
References
-
- Airley, R. E., J. Loncaster, J. A. Raleigh, A. L. Harris, S. E. Davidson, R. D. Hunter, C. M. West, and I. J. Stratford. 2003. GLUT-1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in carcinoma of the cervix: relationship to pimonidazole binding. Int. J. Cancer 104:85-91. - PubMed
-
- Almeida, A., S. Moncada, and J. P. Bolanos. 2004. Nitric oxide switches on glycolysis through the AMP protein kinase and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:45-51. - PubMed
-
- Arcasoy, M. O., K. Amin, S. C. Chou, Z. A. Haroon, M. Varia, and J. A. Raleigh. 2005. Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor expression in head and neck cancer: relationship to tumor hypoxia. Clin. Cancer Res. 11:20-27. - PubMed
-
- Barabasi, A. L., and Z. N. Oltvai. 2004. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5:101-113. - PubMed
-
- Beauloye, C., A. S. Marsin, L. Bertrand, U. Krause, D. G. Hardie, J. L. Vanoverschelde, and L. Hue. 2001. Insulin antagonizes AMP-activated protein kinase activation by ischemia or anoxia in rat hearts, without affecting total adenine nucleotides. FEBS Lett. 505:348-352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
