Cyclin D1 determines mitochondrial function in vivo
- PMID: 16809779
- PMCID: PMC1592725
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02074-05
Cyclin D1 determines mitochondrial function in vivo
Abstract
The cyclin D1 gene encodes a regulatory subunit of the holoenzyme that phosphorylates and inactivates the pRb tumor suppressor to promote nuclear DNA synthesis. cyclin D1 is overexpressed in human breast cancers and is sufficient for the development of murine mammary tumors. Herein, cyclin D1 is shown to perform a novel function, inhibiting mitochondrial function and size. Mitochondrial activity was enhanced by genetic deletion or antisense or small interfering RNA to cyclin D1. Global gene expression profiling and functional analysis of mammary epithelial cell-targeted cyclin D1 antisense transgenics demonstrated that cyclin D1 inhibits mitochondrial activity and aerobic glycolysis in vivo. Reciprocal regulation of these genes was observed in cyclin D1-induced mammary tumors. Cyclin D1 thus integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function.
Figures
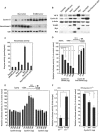
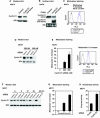
 , P < 0.05; n = 10). (E) Luciferase activity of hexokinase II promoter in response to cyclin D3, cyclin A, and cyclin E in transfected NAFA cells. Data are compared to relevant empty vector and displayed as means ± SEM (n = 4). (F) Hexokinase II promoter activity was assessed in either 3T3 cells, cyclin D1−/− 3T3 cells, or cyclin D1−/− 3T3 cells with transfected cyclin D1 expression plasmid, in each case normalized to Renilla luciferase or β-galactosidase activity, as means ± SEM (
, P < 0.05; n = 10). (E) Luciferase activity of hexokinase II promoter in response to cyclin D3, cyclin A, and cyclin E in transfected NAFA cells. Data are compared to relevant empty vector and displayed as means ± SEM (n = 4). (F) Hexokinase II promoter activity was assessed in either 3T3 cells, cyclin D1−/− 3T3 cells, or cyclin D1−/− 3T3 cells with transfected cyclin D1 expression plasmid, in each case normalized to Renilla luciferase or β-galactosidase activity, as means ± SEM ( , P < 0.05; n ≥ 20). HK II, hexokinase II.
, P < 0.05; n ≥ 20). HK II, hexokinase II.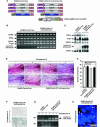
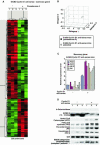


References
-
- Albanese, C., M. D'Amico, A. T. Reutens, M. Fu, G. Watanabe, R. J. Lee, R. N. Kitsis, B. Henglein, M. Avantaggiati, K. Somasundaram, B. Thimmapaya, and R. G. Pestell. 1999. Activation of the cyclin D1 gene by the E1A-associated protein p300 through AP-1 inhibits cellular apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 274:34186-34195. - PubMed
-
- Albanese, C., J. Hulit, T. Sakamaki, and R. G. Pestell. 2002. Recent advances in inducible expression in transgenic mice. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:129-141. - PubMed
-
- Albanese, C., A. T. Reutens, B. Bouzahzah, M. Fu, M. D'Amico, T. Link, R. Nicholson, R. A. Depinho, and R. G. Pestell. 2000. Sustained mammary gland-directed, ponasterone A-inducible expression in transgenic mice. FASEB J. 14:877-884. - PubMed
-
- Albanese, C., K. Wu, M. D'Amico, C. Jarrett, D. Joyce, J. Hughes, J. Hulit, T. Sakamaki, M. Fu, A. Ben-Ze'ev, J. F. Bromberg, C. Lamberti, U. Verma, R. B. Gaynor, S. W. Byers, and R. G. Pestell. 2003. IKKalpha regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf. Mol. Biol. Cell 14:585-599. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh, A. A., M. B. Eisen, R. E. Davis, C. Ma, I. S. Lossos, A. Rosenwald, J. C. Boldrick, H. Sabet, T. Tran, X. Yu, J. I. Powell, L. Yang, G. E. Marti, T. Moore, J. Hudson, Jr., L. Lu, D. B. Lewis, R. Tibshirani, G. Sherlock, W. C. Chan, T. C. Greiner, D. D. Weisenburger, J. O. Armitage, R. Warnke, R. Levy, W. Wilson, M. R. Grever, J. C. Byrd, D. Botstein, P. O. Brown, and L. M. Staudt. 2000. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503-511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA075503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA56036/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03AG20337/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA75503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093596/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA93596/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA051008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA070896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA51008-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA107382/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA70896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA86072/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA086072/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107382/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA056036/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
