An antagonistic function for Arabidopsis DCL2 in development and a new function for DCL4 in generating viral siRNAs
- PMID: 16810317
- PMCID: PMC1523179
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601217
An antagonistic function for Arabidopsis DCL2 in development and a new function for DCL4 in generating viral siRNAs
Abstract
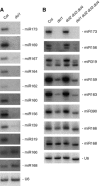
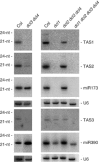
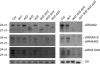
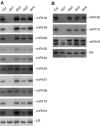
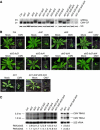
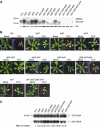
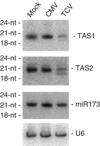
Plants contain more DICER-LIKE (DCL) enzymes and double-stranded RNA binding (DRB) proteins than other eukaryotes, resulting in increased small RNA network complexities. Analyses of single, double, triple and quadruple dcl mutants exposed DCL1 as a sophisticated enzyme capable of producing both microRNAs (miRNAs) and siRNAs, unlike the three other DCLs, which only produce siRNAs. Depletion of siRNA-specific DCLs results in unbalanced small RNA levels, indicating a redeployment of DCL/DRB complexes. In particular, DCL2 antagonizes the production of miRNAs and siRNAs by DCL1 in certain circumstances and affects development deleteriously in dcl1 dcl4 and dcl1 dcl3 dcl4 mutant plants, whereas dcl1 dcl2 dcl3 dcl4 quadruple mutant plants are viable. We also show that viral siRNAs are produced by DCL4, and that DCL2 can substitute for DCL4 when this latter activity is reduced or inhibited by viruses, pointing to the competitiveness of DCL2. Given the complexity of the small RNA repertoire in plants, the implication of each DCL, in particular DCL2, in the production of small RNAs that have no known function will constitute one of the next challenges.
Figures


References
-
- Adenot X, Elmayan T, Lauressergues D, Boutet S, Bouché N, Gasciolli V, Vaucheret H (2006) Uncoupled production of ta-siRNAs in hypomorphic rdr6 and sgs3 mutants uncovers a role for TAS3 in AGO7-DCL4-DRB4-mediated control of leaf morphology. Curr Biol 16: 927–932 - PubMed
-
- Béclin C, Boutet S, Waterhouse P, Vaucheret H (2002) A branched pathway for transgene-induced RNA silencing in plants. Curr Biol 12: 684–688 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

