Urine proteomic profiling of pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 16810512
- PMCID: PMC1538636
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-006-0165-8
Urine proteomic profiling of pediatric nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
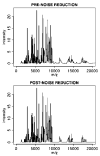
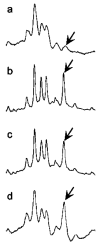
The prognosis of pediatric nephrotic syndrome (NS) correlates with the responsiveness to glucocorticoid therapy. Steroid-resistant NS (SRNS) patients progress to end-stage renal disease, while steroid-sensitive NS (SSNS) and steroid-dependent (SDNS) patients do not. We have performed proteomic profiling of urine samples from a cross section of pediatric and adolescent subjects with SSNS, SRNS, and orthostatic proteinuria (OP) to identify urinary biomarkers of steroid resistance. We performed surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF MS) on urine from 19 subjects with SSNS/SDNS in remission, 14 with SSNS/SDNS in relapse, 5 with SRNS in relapse, and 6 with OP. Genetic algorithm search of principal component space revealed a group of five peaks distinguishing SRNS subjects, with mass/charge (m/z) values of 3,917.07, 4,155.53, 6,329.68, 7,036.96, and 11,117.4. Our analyses identified the peak at m/z 11,117.4 with an accuracy of 95% for classifying SRNS. Multidimensional protein fractionation and mass spectrometric analysis of SRNS urine samples combined with immunodepletion identified the 11,117.4 protein as beta2-microglobulin (B2M). Using an unbiased protein profiling approach, we have validated previously reported findings of B2M as a biomarker associated with SRNS. Prospective studies are warranted to establish additional biomarkers that would be predictive of SRNS.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic profiling identifies haptoglobin as a potential serum biomarker for steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome.Am J Nephrol. 2012;36(2):105-13. doi: 10.1159/000339755. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Am J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22759352
-
Urinary proteome of steroid-sensitive and steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood.Am J Nephrol. 2006;26(3):258-67. doi: 10.1159/000093814. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Am J Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16763371 Clinical Trial.
-
Follow-up of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: tubular proteinuria and enzymuria.Pediatr Nephrol. 2000 Dec;15(3-4):252-8. doi: 10.1007/s004670000472. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 11149121 Clinical Trial.
-
Urine proteomic profiling to identify biomarkers of steroid resistance in pediatric nephrotic syndrome.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008 Oct;5(5):715-9. doi: 10.1586/14789450.5.5.715. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18937561 Review.
-
Exploring the Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome: The PodoNet Registry.Front Pediatr. 2018 Jul 17;6:200. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00200. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30065916 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics profiling of urine with surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry.Proteome Sci. 2007 Jan 15;5:2. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-5-2. Proteome Sci. 2007. PMID: 17224053 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Biomarker Panel to Identify Steroid Resistance in Childhood Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome.Biomark Insights. 2017 Mar 8;12:1177271917695832. doi: 10.1177/1177271917695832. eCollection 2017. Biomark Insights. 2017. PMID: 28469399 Free PMC article.
-
Urine collected from diapers can be used for 2-D PAGE in infants and young children.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2009 Aug;3(8):989-99. doi: 10.1002/prca.200900045. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2009. PMID: 21137001 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in proteomic profiling of pediatric kidney diseases.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Oct;37(10):2255-2265. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05497-2. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35220505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining nephrotic syndrome from an integrative genomics perspective.Pediatr Nephrol. 2015 Jan;30(1):51-63; quiz 59. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-2857-9. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 24890338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hogg RJ, Portman RJ, Milliner D, Lemley KV, Eddy A, Ingelfinger J. Evaluation and management of proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome in children: recommendations from a pediatric nephrology panel established at the National Kidney Foundation conference on proteinuria, albuminuria, risk, assessment, detection, and elimination (PARADE) Pediatrics. 2000;105:1242–1249. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Bellew CA, Silverstein DM, Aviles DH, Boineau FG, Vehaskari VM. High incidence of initial and late steroid resistance in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1275–1281. - PubMed
-
- Schlesinger ER, Sultz HA, Mosher WE, Feldman JG. The nephrotic syndrome. Its incidence and implications for the community. Am J Dis Child. 1968;116:623–632. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava T, Simon SD, Alon US. High incidence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:13–18. - PubMed
-
- The primary nephrotic syndrome in children. Identification of patients with minimal change nephrotic syndrome from initial response to prednisone. A report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. J Pediatr. 1981;98:561–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

