Detection of H. pylori antibody profile in serum by protein array
- PMID: 16810756
- PMCID: PMC4087718
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i25.4044
Detection of H. pylori antibody profile in serum by protein array
Abstract
Aim: To detect multiple H. pylori antibodies in serum samples of individuals who carry H. pylori by protein array.
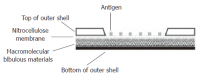
Methods: Recombinant H. pylori antigens, urease B subunit (UreB), vacuolating toxin A (VacA) and cytotoxin associated gene A protein (CagA), were prepared and immobilized in matrixes on nitrocellulose membrane by robotics to bind the specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies in serum. Staphylococcus protein A (SPA) labeled by colloid gold was used to integrate the immuno-complex and gave red color signal. The scanner based on charge-coupled device (CCD) could collect the image signal and convert it into digital signal.
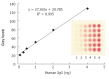
Results: When human IgG was printed on the membrane in increasing concentrations and incubated with immunogold, a linear dose response curve was obtained and the detection limit for IgG was about 0.025 ng. The cutoff values, which were defined as the mean grey level plus 3 times of standard deviation, were 27.183, 28.546 and 27.402, for anti-UreB IgG, anti-CagA IgG and anti-VacA IgG, respectively, as 400 human serum samples with negative H. pylori antibodies were detected by the protein array. When 180 serum samples from patients in hospital were employed for detection of IgG against UreB, CagA and VacA, the sensitivity of the protein array was 93.4%, 95.4%, 96.0%, and the specificity was 94.8%, 94.4% and 97.5%, respectively, as compared with the results obtained by ELISA. The assay also showed high reproducibility, uniformity and stability, and the results were available within 30 min.
Conclusion: The protein array is a very practical method for rapid detection of multiple antibodies in serum samples. It is especially useful for large scale epidemiological investigation of the infection of H. pylori.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Value of protein array in the diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori infection in children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;13(9):728-31. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21924022 Chinese.
-
Frequencies of the expression of main protein antigens from Helicobacter pylori isolates and production of specific serum antibodies in infected patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan 21;11(3):421-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i3.421. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15637759 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of Western Blot method for the detection of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori antigens in patients with gastric carcinoma and cases with epigastric complaints].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010 Jan;44(1):21-8. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010. PMID: 20455395 Turkish.
-
[Evaluation of western blot methods for serologic diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infections].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002 Apr;36(2):153-60. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002. PMID: 12652867 Turkish.
-
[Helicobacter pylori genotypes and their association with host's immune response].Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2002 Jul-Sep;67(3):155-60. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2002. PMID: 12653051 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive diagnostic tests for Helicobacter pylori infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 15;3(3):CD012080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012080.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29543326 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Consensus Report on Family-Based Helicobacter pylori Infection Control and Management (2021 Edition).Gut. 2022 Feb;71(2):238-253. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325630. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Gut. 2022. PMID: 34836916 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of an Iranian Home-made Helicobacter pylori Stool Antigen ELISA Kit.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014 Jun;7(6):e10629. doi: 10.5812/jjm.10629. Epub 2014 Jun 1. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25371803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Israel DA, Peek RM. pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1271–1290. - PubMed
-
- Sanders MK, Peura DA. Helicobacter pylori-Associated Diseases. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002;4:448–454. - PubMed
-
- Blaser MJ. Linking Helicobacter pylori to gastric cancer. Nat Med. 2000;6:376–377. - PubMed
-
- Unger Z, Molnár B, Prónai L, Szaleczky E, Zágoni T, Tulassay Z. Mutant p53 expression and apoptotic activity of Helicobacter pylori positive and negative gastritis in correlation with the presence of intestinal metaplasia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15:389–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

