Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach
- PMID: 16814713
- PMCID: PMC3026384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.030
Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach
Abstract
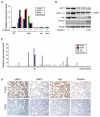
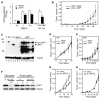
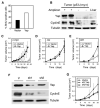
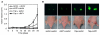
The heterogeneity and instability of human tumors hamper straightforward identification of cancer-causing mutations through genomic approaches alone. Herein we describe a mouse model of liver cancer initiated from progenitor cells harboring defined cancer-predisposing lesions. Genome-wide analyses of tumors in this mouse model and in human hepatocellular carcinomas revealed a recurrent amplification at mouse chromosome 9qA1, the syntenic region of human chromosome 11q22. Gene-expression analyses delineated cIAP1, a known inhibitor of apoptosis, and Yap, a transcription factor, as candidate oncogenes in the amplicon. In the genetic context of their amplification, both cIAP1 and Yap accelerated tumorigenesis and were required to sustain rapid growth of amplicon-containing tumors. Furthermore, cIAP1 and Yap cooperated to promote tumorigenesis. Our results establish a tractable model of liver cancer, identify two oncogenes that cooperate by virtue of their coamplification in the same genomic locus, and suggest an efficient strategy for the annotation of human cancer genes.
Figures
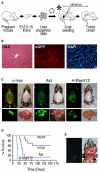
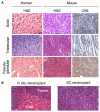
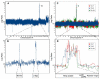
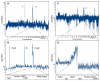
Comment in
-
Cross-species oncogenomics in cancer gene identification.Cell. 2006 Jun 30;125(7):1230-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.018. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16814709
References
-
- Aguilar F, Harris CC, Sun T, Hollstein M, Cerutti P. Geographic variation of p53 mutational profile in nonmalignant human liver. Science. 1994;264:1317–1319. - PubMed
-
- Artandi SE, Depinho RA. Mice without telomerase: what can they teach us about human cancer? Nat. Med. 2000;6:852–855. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Totty NF, Irwin MS, Sudol M, Downward J. Akt phosphorylates the Yes-associated protein, YAP, to induce interaction with 14–3-3 and attenuation of p73-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:11–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

