Structure-based model of the stepping motor of PcrA helicase
- PMID: 16815905
- PMCID: PMC1557568
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.088203
Structure-based model of the stepping motor of PcrA helicase
Abstract
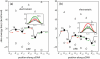
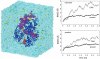
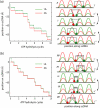
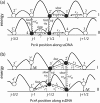
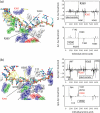
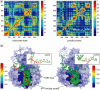
DNA helicases are ubiquitous molecular motors involved in cellular DNA metabolism. They move along single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and separate duplex DNA into its component strands, utilizing the free energy from ATP hydrolysis. The PcrA helicase from Bacillus stearothermophilus translocates as a monomer progressively from the 3' end to the 5' end of ssDNA and is one of the smallest motor proteins structurally known in full atomic detail. Using high-resolution crystal structures of the PcrA-DNA complex, we performed nanosecond molecular dynamics simulations and derived potential energy profiles governing individual domain movement of the PcrA helicase along ssDNA. Based on these profiles, the millisecond translocation of the helicase along ssDNA was described through Langevin dynamics. The calculations support a domain stepping mechanism of PcrA helicase, in which, during one ATP hydrolysis cycle, the pulling together and pushing apart of domains 2A and 1A are synchronized with alternating mobilities of the individual domains in such a fashion that PcrA moves unidirectionally along ssDNA. By combining short timescale (nanoseconds) molecular dynamics and long timescale (milliseconds) stochastic-dynamics descriptions, our study suggests a structure-based mechanism of the ATP-powered unidirectional movement of PcrA helicase.
Figures



Similar articles
-
How directional translocation is regulated in a DNA helicase motor.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 1;93(11):3783-97. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.109546. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17704159 Free PMC article.
-
PcrA helicase, a prototype ATP-driven molecular motor.Structure. 2006 Sep;14(9):1345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.06.017. Structure. 2006. PMID: 16962966
-
The study of interactions between DNA and PcrA DNA helicase by using targeted molecular dynamic simulations.J Mol Model. 2013 Nov;19(11):4997-5006. doi: 10.1007/s00894-013-2008-4. Epub 2013 Sep 26. J Mol Model. 2013. PMID: 24068309
-
Coordination and control inside simple biomolecular machines.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;805:353-84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-02970-2_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24446369 Review.
-
On helicases and other motor proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Apr;18(2):243-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.01.007. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18329872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tautomerisation Mechanisms in the Adenine-Thymine Nucleobase Pair during DNA Strand Separation.J Phys Chem B. 2023 May 18;127(19):4220-4228. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c08631. Epub 2023 Mar 20. J Phys Chem B. 2023. PMID: 36939840 Free PMC article.
-
Proton transfer during DNA strand separation as a source of mutagenic guanine-cytosine tautomers.Commun Chem. 2022 Nov 5;5(1):144. doi: 10.1038/s42004-022-00760-x. Commun Chem. 2022. PMID: 36697962 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule nanometry for biological physics.Rep Prog Phys. 2013 Jan;76(1):016601. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/76/1/016601. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Rep Prog Phys. 2013. PMID: 23249673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How directional translocation is regulated in a DNA helicase motor.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 1;93(11):3783-97. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.109546. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17704159 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the human RECQ1 helicase reveals a putative strand-separation pin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 27;106(4):1039-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806908106. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19151156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohman, T., and K. Bjornson. 1996. Mechanisms of helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65:169–214. - PubMed
-
- Bird, L., S. Subramanya, and D. Wigley. 1998. Helicases: a unifying structural theme. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8:14–18. - PubMed
-
- Waksman, G., E. Lanka, and J. Carazo. 2000. Helicases as nucleic acid unwinding machines. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Marians, K. 2001. Crawling and wiggling on DNA: structural insights to the mechanism of DNA unwinding by helicases. Structure. 8:R227–R235. - PubMed
-
- Caruthers, J., and D. McKay. 2002. Helicase structure and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12:123–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

