Glucose modulates [Ca2+]i oscillations in pancreatic islets via ionic and glycolytic mechanisms
- PMID: 16815907
- PMCID: PMC1557567
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.087296
Glucose modulates [Ca2+]i oscillations in pancreatic islets via ionic and glycolytic mechanisms
Abstract
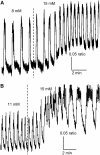
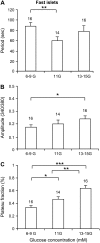
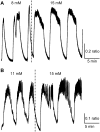
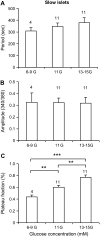
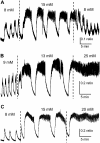
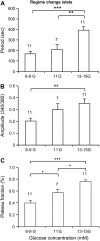
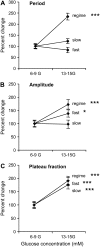
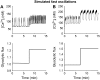
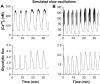
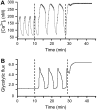
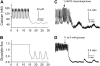
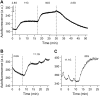
Pancreatic islets of Langerhans display complex intracellular calcium changes in response to glucose that include fast (seconds), slow ( approximately 5 min), and mixed fast/slow oscillations; the slow and mixed oscillations are likely responsible for the pulses of plasma insulin observed in vivo. To better understand the mechanisms underlying these diverse patterns, we systematically analyzed the effects of glucose on period, amplitude, and plateau fraction (the fraction of time spent in the active phase) of the various regimes of calcium oscillations. We found that in both fast and slow islets, increasing glucose had limited effects on amplitude and period, but increased plateau fraction. In some islets, however, glucose caused a major shift in the amplitude and period of oscillations, which we attribute to a conversion between ionic and glycolytic modes (i.e., regime change). Raising glucose increased the plateau fraction equally in fast, slow, and regime-changing islets. A mathematical model of the pancreatic islet consisting of an ionic subsystem interacting with a slower metabolic oscillatory subsystem can account for these complex islet calcium oscillations by modifying the relative contributions of oscillatory metabolism and oscillatory ionic mechanisms to electrical activity, with coupling occurring via K(ATP) channels.
Figures

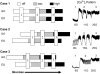
References
-
- Hellerstrom, C. 1967. Effects of carbohydrates on the oxygen consumption of isolated pancreatic islets of mice. Endocrinology. 81:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Hutton, J. C., and W. J. Malaisse. 1980. Dynamics of O2 consumption in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 18:395–405. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft, F. M., and P. Rorsman. 1989. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 54:87–143. - PubMed
-
- Bratusch-Marrain, P. R., M. Komjati, and W. K. Waldhausl. 1986. Efficacy of pulsatile versus continuous insulin administration on hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization in type 1 diabetic humans. Diabetes. 35:922–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

