Cardioprotection by postconditioning in conscious rats is limited to coronary occlusions <45 min
- PMID: 16815986
- PMCID: PMC3741072
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00479.2006
Cardioprotection by postconditioning in conscious rats is limited to coronary occlusions <45 min
Abstract
Objectives: Brief episodes of ischemia and reperfusion after a lethal ischemic insult confer cardioprotection, a phenomenon termed "ischemic postconditioning." However, all studies reported to date have been conducted in open-chest animal models. We sought to determine whether postconditioning occurs in conscious animals and whether it protects against severe myocardial injury.
Methods: Chronically instrumented rats were assigned to a 30- (Subset 1), 45- (Subset 2), or 60-min (Subset 3) coronary occlusion followed by 24 h of reperfusion. In each subset, rats received no further intervention (control), were preconditioned with 12 cycles of 2-min occlusion/2-min reperfusion immediately (early preconditioning; EPC) or 24 h (late preconditioning; LPC) before myocardial infarction, or were postconditioned with 20 cycles of 10-s occlusion/10-s reperfusion immediately after myocardial infarction (20-10 PostC).
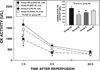
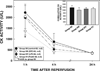
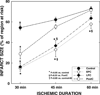
Results: With a 30-min occlusion, infarct size (54.4 +/- 2.3% of risk region in control-30) was significantly reduced in EPC-30, LPC-30, and 20-10 PostC-30 groups (by 72, 70, and 47%, respectively; all P < 0.05 vs. control-30). With a 45-min occlusion, infarct size (62.2 +/- 2.4% in control-45) was reduced in EPC-45 and LPC-45 groups (by 47 and 41%, respectively; all P < 0.05 vs. control-45) but not in the 20-10 PostC-45 group [55.4 +/- 2.3%, P = not significant (NS) vs. control-45]. With a 60-min occlusion, infarct size (72.7 +/- 2.2% in control-60) was reduced in the EPC-60 (by 20%, P < 0.05) but not in the LPC-60 (63.6 +/- 2.5%, P = NS) or in the 20-20 PostC group (71.5 +/- 3.4%, P = NS).
Conclusions: Both early and late ischemic preconditioning as well as ischemic postconditioning confer protection in conscious rats; however, unlike early preconditioning, postconditioning protects only against coronary occlusions <45 min. In the conscious rat, the cardioprotection afforded by postconditioning is limited to mild to moderate myocardial injury.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The cardioprotection of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning is enhanced by postconditioning via a COX-2-mediated mechanism in conscious rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):H2557-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17704286 Free PMC article.
-
Remote postconditioning. Brief renal ischemia and reperfusion applied before coronary artery reperfusion reduces myocardial infarct size via endogenous activation of adenosine receptors.Basic Res Cardiol. 2005 Sep;100(5):404-12. doi: 10.1007/s00395-005-0539-2. Epub 2005 Jun 17. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 15965583
-
Helium-induced cardioprotection of healthy and hypertensive rat myocardium in vivo.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 5;684(1-3):125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.03.045. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22497999
-
[Reperfusion and postconditioning in acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. A new paradigm for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. From bench to bedside?].Arch Cardiol Mex. 2006 Oct-Dec;76 Suppl 4:S76-101. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2006. PMID: 17469337 Review. Spanish.
-
Realizing the clinical potential of ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Nov;2(11):568-75. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio0346. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2005. PMID: 16258568 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical effect of postconditioning in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Mar;16(3):198-207. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1400237. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015. PMID: 25743121 Free PMC article.
-
Post-ischemic conditioning in the rat retina is dependent upon ischemia duration and is not additive with ischemic pre-conditioning.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Dec;91(6):844-52. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.06.015. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20599964 Free PMC article.
-
The cardioprotection of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning is enhanced by postconditioning via a COX-2-mediated mechanism in conscious rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):H2557-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17704286 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of ischemic postconditioning against ischemia reperfusion-induced myocardium oxidative injury in IR rats.Molecules. 2012 Mar 27;17(4):3805-17. doi: 10.3390/molecules17043805. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22453931 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial dysfunction in the periinfarct and remote regions following anterior infarction in rats quantified by 2D radial strain echocardiography: an observational cohort study.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008 Apr 29;6:17. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-6-17. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008. PMID: 18445286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argaud L, Gateau-Roesch O, Raisky O, Loufouat J, Robert D, Ovize M. Postconditioning inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition. Circulation. 2005;111:194–197. - PubMed
-
- Baker JE, Konorev EA, Gross GJ, Chilian WM, Jacob HJ. Resistance to myocardial ischemia in five rat strains: is there a genetic component of cardioprotection? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;278:H1395–H1400. - PubMed
-
- Bolli R. The late phase of preconditioning. Circ Res. 2000;87:972–983. - PubMed
-
- Chiari PC, Bienengraeber MW, Pagel PS, Krolikowski JG, Kersten JR, Warltier DC. Isoflurane protects against myocardial infarction during early reperfusion by activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signal transduction: evidence for anesthetic-induced postconditioning in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 2005;102:102–109. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MV, Downey JM. Myocardial preconditioning promises to be a novel approach to the treatment of ischemic heart disease. Annu Rev Med. 1996;47:21–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-55757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-68088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-70897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-76794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-74351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-78825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

