What is the functional significance of chronic stress-induced CA3 dendritic retraction within the hippocampus?
- PMID: 16816092
- PMCID: PMC1512384
- DOI: 10.1177/1534582306289043
What is the functional significance of chronic stress-induced CA3 dendritic retraction within the hippocampus?
Abstract
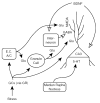
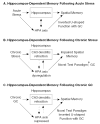
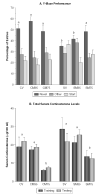
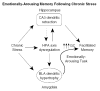
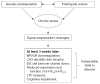
Chronic stress produces consistent and reversible changes within the dendritic arbors of CA3 hippocampal neurons, characterized by decreased dendritic length and reduced branch number. This chronic stress-induced dendritic retraction has traditionally corresponded to hippocampus-dependent spatial memory deficits. However, anomalous findings have raised doubts as to whether a CA3 dendritic retraction is sufficient to compromise hippocampal function. The purpose of this review is to outline the mechanism underlying chronic stress-induced CA3 dendritic retraction and to explain why CA3 dendritic retraction has been thought to mediate spatial memory. The anomalous findings provide support for a modified hypothesis, in which chronic stress is proposed to induce CA3 dendritic retraction, which then disrupts hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity, leading to dysregulated glucocorticoid release. The combination of hippocampal CA3 dendritic retraction and elevated glucocorticoid release contributes to impaired spatial memory. These findings are presented in the context of clinical conditions associated with elevated glucocorticoids.
Figures
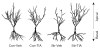
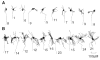
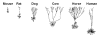


Similar articles
-
Chronic stress and hippocampal dendritic complexity: Methodological and functional considerations.Physiol Behav. 2017 Sep 1;178:66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Physiol Behav. 2017. PMID: 27887995 Review.
-
Homeostatic maintenance in excitability of tree shrew hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons after chronic stress.Hippocampus. 2004;14(6):742-51. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10212. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15318332
-
Chronic social stress reduces dendritic arbors in CA3 of hippocampus and decreases binding to serotonin transporter sites.Synapse. 2000 May;36(2):85-94. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(200005)36:2<85::AID-SYN1>3.0.CO;2-Y. Synapse. 2000. PMID: 10767055
-
Chronic glucocorticoids increase hippocampal vulnerability to neurotoxicity under conditions that produce CA3 dendritic retraction but fail to impair spatial recognition memory.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 1;27(31):8278-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2121-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17670974 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stress-induced hippocampal vulnerability: the glucocorticoid vulnerability hypothesis.Rev Neurosci. 2008;19(6):395-411. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2008.19.6.395. Rev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19317179 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Out of my real body: cognitive neuroscience meets eating disorders.Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 May 6;8:236. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00236. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24834042 Free PMC article.
-
Forebrain CRHR1 deficiency attenuates chronic stress-induced cognitive deficits and dendritic remodeling.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Jun;42(3):300-10. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.020. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 21296667 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and perhaps estradiol protect against corticosterone-induced hippocampal CA3 dendritic retraction in gonadectomized female and male rats.Neuroscience. 2013 Aug 29;246:409-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.04.027. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23618757 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid modulation of chronic mild stress-induced selective enhancement of trace fear conditioning in adolescent rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;27(10):947-55. doi: 10.1177/0269881113499207. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23926242 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerability to depression: from brain neuroplasticity to identification of biomarkers.J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 7;31(36):12889-99. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1309-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21900567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akirav I, Sandi C, Richter-Levin G. Differential activation of hippocampus and amygdala following spatial learning under stress. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2001;14:719–725. - PubMed
-
- Albeck DS, Hastings NB, McEwen BS. Effects of adrenalectomy and Type I or Type II glucocorticoid receptor activation on AVP and CRH mRNA in the rat hippocampus. Molecular Brain Research. 1994;26:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Arbel I, Kadar T, Silbermann M, Levy A. The effects of long-term corticosterone administration on hippocampal morphology and cognitive performance of middle-aged rats. Brain Research. 1994;657:227–235. - PubMed
-
- Aus Der Mühlen K, Ockenfels H. Morphologische Veränderungen im Diencephalon und Telencephalon nach Störungen des Regelkreisis Adenohypophyse-Nebennierenrinde [Morphological changes in the diencephalon and telencephalon following disturbances to the feedback mechanism adenohypophysis-adrenal cortex]. Z. Zellforsch. 1969;93:126–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
