H-NS represses inv transcription in Yersinia enterocolitica through competition with RovA and interaction with YmoA
- PMID: 16816182
- PMCID: PMC1539963
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00862-05
H-NS represses inv transcription in Yersinia enterocolitica through competition with RovA and interaction with YmoA
Abstract
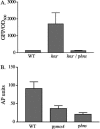
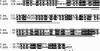
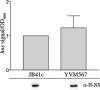
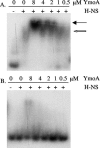
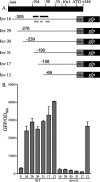
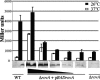
Yersinia enterocolitica is able to efficiently invade Peyer's patches with the aid of invasin, an outer member protein involved in the attachment and invasion of M cells. Invasin is encoded by inv, which is positively regulated by RovA in both Y. enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis while negatively regulated by YmoA in Y. enterocolitica and H-NS in Y. pseudotuberculosis. In this study we present data indicating H-NS and RovA bind directly and specifically to the inv promoter of Y. enterocolitica. We also show that RovA and H-NS from Y. enterocolitica bind to a similar region of the inv promoter and suggest they compete for binding sites. This is similar to recently published data from Y. pseudotuberculosis, revealing a potentially conserved mechanism of inv regulation between Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Furthermore, we present data suggesting H-NS and YmoA form a repression complex on the inv promoter, with H-NS providing the binding specificity and YmoA interacting with H-NS to form a repression complex. We also demonstrate that deletion of the predicted H-NS binding region relieves the requirement for RovA-dependent transcription of the inv promoter, consistent with RovA acting as a derepressor of H-NS-mediated repression. Levels of H-NS and YmoA are similar between 26 degrees C and 37 degrees C, suggesting that the H-NS/YmoA repression complex is present at both temperatures, while the levels of rovA transcript are low at 37 degrees C and high at 26 degrees C, leading to expression of inv at 26 degrees C. Expression of RovA at 37 degrees C results in transcription of inv and production of invasin. Data presented here support a model of inv regulation where the level of RovA within the cell governs inv expression. As RovA levels increase, RovA can successfully compete for binding to the inv promoter with the H-NS/YmoA complex, resulting in derepression of inv transcription.
Figures


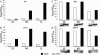
Similar articles
-
RovA is autoregulated and antagonizes H-NS-mediated silencing of invasin and rovA expression in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Aug;53(3):871-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04162.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15255899
-
Comparative analysis of the regulation of rovA from the pathogenic yersiniae.J Bacteriol. 2007 Aug;189(16):5963-75. doi: 10.1128/JB.00528-07. Epub 2007 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17573476 Free PMC article.
-
The RovA regulons of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis are distinct: evidence that many RovA-regulated genes were acquired more recently than the core genome.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Oct;66(1):189-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05907.x. Epub 2007 Sep 3. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17784909
-
Regulatory elements implicated in the environmental control of invasin expression in enteropathogenic Yersinia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:156-66. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966412 Review.
-
Invasin and beyond: regulation of Yersinia virulence by RovA.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Jun;12(6):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.04.006. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15165608 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of horizontally acquired genes by the Hha-YdgT proteins in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):1152-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.01206-07. Epub 2007 Nov 26. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18039769 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Yersinia enterocolitica pYV-encoded type III secretion system is modulated by lipopolysaccharide O-antigen status.Infect Immun. 2007 Mar;75(3):1512-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00942-06. Epub 2006 Dec 18. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17178779 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of MarR family transcription factors as counter-silencers in regulatory networks.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020 Jun;55:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32044654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of the HRM method for identifying possible mutations in the ymoA gene region and evaluating their influence on the enterotoxic properties of Y. enterocolitica strains.BMC Vet Res. 2014 Sep 19;10:207. doi: 10.1186/s12917-014-0207-6. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25234736 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into transcriptional regulation by H-NS.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008 Apr;11(2):113-20. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.02.011. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18387844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
-
- Beloin, C., and C. J. Dorman. 2003. An extended role for the nucleoid structuring protein H-NS in the virulence gene regulatory cascade of Shigella flexneri. Mol. Microbiol. 47:825-838. - PubMed
-
- Buchmeier, N., S. Bossie, C. Y. Chen, F. C. Fang, D. G. Guiney, and S. J. Libby. 1997. SlyA, a transcriptional regulator of Salmonella typhimurium, is required for resistance to oxidative stress and is expressed in the intracellular environment of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 65:3725-3730. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

