Ubiquitin-like protein 5 positively regulates chaperone gene expression in the mitochondrial unfolded protein response
- PMID: 16816413
- PMCID: PMC1569816
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.061580
Ubiquitin-like protein 5 positively regulates chaperone gene expression in the mitochondrial unfolded protein response
Abstract
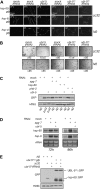
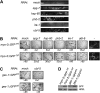
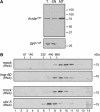
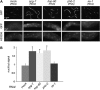
Perturbation of the protein-folding environment in the mitochondrial matrix selectively upregulates the expression of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial chaperones. To identify components of the signal transduction pathway(s) mediating this mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPR(mt)), we first isolated a temperature-sensitive mutation (zc32) that conditionally activates the UPR(mt) in C. elegans and subsequently searched for suppressors by systematic inactivation of genes. RNAi of ubl-5, a gene encoding a ubiquitin-like protein, suppresses activation of the UPR(mt) markers hsp-60::gfp and hsp-6::gfp by the zc32 mutation and by other manipulations that promote mitochondrial protein misfolding. ubl-5 (RNAi) inhibits the induction of endogenous mitochondrial chaperone encoding genes hsp-60 and hsp-6 and compromises the ability of animals to cope with mitochondrial stress. Mitochondrial morphology and assembly of multi-subunit mitochondrial complexes of biotinylated proteins are also perturbed in ubl-5(RNAi) worms, indicating that UBL-5 also counteracts physiological levels of mitochondrial stress. Induction of mitochondrial stress promotes accumulation of GFP-tagged UBL-5 in nuclei of transgenic worms, suggesting that UBL-5 effects a nuclear step required for mounting a response to the threat of mitochondrial protein misfolding.
Figures


References
-
- Artal-Sanz, M., W. Y. Tsang, E. M. Willems, L. A. Grivell, B. D. Lemire et al., 2003. The mitochondrial prohibitin complex is essential for embryonic viability and germline function in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 32091–32099. - PubMed
-
- Beal, M. F., 2005. Mitochondria take center stage in aging and neurodegeneration. Ann. Neurol. 58: 495–505. - PubMed
-
- Biaszczak, A., C. Georgopoulos and K. Liberek, 1999. On the mechanism of FtsH-dependent degradation of the sigma 32 transcriptional regulator of Escherichia coli and the role of the Dnak chaperone machine. Mol. Microbiol. 31: 157–166. - PubMed
-
- Bukau, B., 1993. Regulation of the Escherichia coli heat-shock response. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 671–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

