Human alpha-defensins neutralize toxins of the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase family
- PMID: 16817779
- PMCID: PMC1609915
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060425
Human alpha-defensins neutralize toxins of the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase family
Abstract
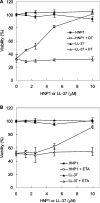
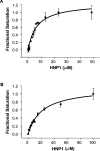
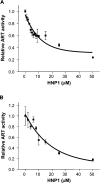
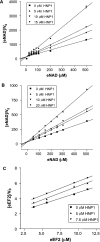
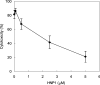
Various bacterial pathogens secrete toxins, which are not only responsible for fatal pathogenesis of disease, but also facilitate evasion of host defences. One of the best-known bacterial toxin groups is the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase family. In the present study, we demonstrate that human neutrophil alpha-defensins are potent inhibitors of the bacterial enzymes, particularly against DT (diphtheria toxin) and ETA (Pseudomonas exotoxin A). HNP1 (human neutrophil protein 1) inhibited DT- or ETA-mediated ADP-ribosylation of eEF2 (eukaryotic elongation factor 2) and protected HeLa cells against DT- or ETA-induced cell death. Kinetic analysis revealed that inhibition of DT and ETA by HNP1 was competitive with respect to eEF2 and uncompetitive against NAD+ substrates. Our results reveal that toxin neutralization represents a novel biological function of HNPs in host defence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transition state structure for ADP-ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 catalyzed by diphtheria toxin.Biochemistry. 2004 Feb 10;43(5):1204-12. doi: 10.1021/bi035907z. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 14756556
-
Investigating the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of sirtuins with NAD analogues and 32P-NAD.Biochemistry. 2009 Apr 7;48(13):2878-90. doi: 10.1021/bi802093g. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19220062
-
Diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A: active-site structure and enzymic mechanism.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;175:27-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76966-5_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1628498 Review. No abstract available.
-
Effect of oxidative stress on in vivo ADP-ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;37(1):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.016. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15381153
-
Molecular mechanisms of the cytotoxicity of ADP-ribosylating toxins.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008;62:271-88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162848. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18785839 Review.
Cited by
-
Human α-Defensin-5 Efficiently Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA, TcdB, and CDT.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 12;11:1204. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01204. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32903430 Free PMC article.
-
Host Cationic Antimicrobial Molecules Inhibit S. aureus Exotoxin Production.mSphere. 2023 Feb 21;8(1):e0057622. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00576-22. Epub 2023 Jan 4. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 36598227 Free PMC article.
-
Functional determinants of human enteric α-defensin HD5: crucial role for hydrophobicity at dimer interface.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):21615-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.367995. Epub 2012 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22573326 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered toxins "zymoxins" are activated by the HCV NS3 protease by removal of an inhibitory protein domain.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 14;6(1):e15916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015916. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21264238 Free PMC article.
-
Clostridium difficile associated infection, diarrhea and colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Apr 7;15(13):1554-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1554. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19340897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corda D., Di Girolamo M. Mono-ADP-ribosylation: a tool for modulating immune response and cell signaling. Science STKE 2002. 2002:PE53. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki I. J., Moss J. Mono-ADP-ribosylation: a reversible posttranslational modification of proteins. Adv. Pharmacol. 1996;35:247–280. - PubMed
-
- Domenighini M., Rappuoli R. Three conserved consensus sequences identify the NAD-binding site of ADP-ribosylating enzymes, expressed by eukaryotes, bacteria and T-even bacteriophages. Mol. Microbiol. 1996;21:667–674. - PubMed
-
- Han S., Tainer J. A. The ARTT motif and a unified structural understanding of substrate recognition in ADP-ribosylating bacterial toxins and eukaryotic ADP-ribosyltransferases. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002;291:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Collier R. J. Understanding the mode of action of diphtheria toxin: a perspective on progress during the 20th century. Toxicon. 2001;39:1793–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

