Inhibition of HIV Env binding to cellular receptors by monoclonal antibody 2G12 as probed by Fc-tagged gp120
- PMID: 16817962
- PMCID: PMC1543650
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-39
Inhibition of HIV Env binding to cellular receptors by monoclonal antibody 2G12 as probed by Fc-tagged gp120
Erratum in
- Retrovirology. 2007;4:23
Abstract
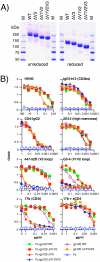
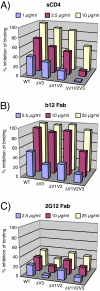
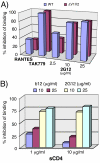
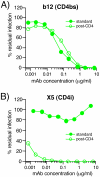
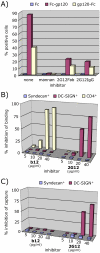
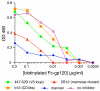
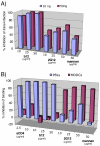
During natural HIV infection, an array of host receptors are thought to influence virus attachment and the kinetics of infection. In this study, to probe the interactions of HIV envelope (Env) with various receptors, we assessed the inhibitory properties of various anti-Env monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in binding assays. To assist in detecting Env in attachment assays, we generated Fc fusions of full-length wild-type gp120 and several variable loop-deleted gp120s. Through investigation of the inhibition of Env binding to cell lines expressing CD4, CCR5, DC-SIGN, syndecans or combinations thereof, we found that the broadly neutralizing mAb, 2G12, directed to a unique carbohydrate epitope of gp120, inhibited Env-CCR5 binding, partially inhibited Env-DC-SIGN binding, but had no effect on Env-syndecan association. Furthermore, 2G12 inhibited Env attachment to primary monocyte-derived dendritic cells, that expressed CD4 and CCR5 primary HIV receptors, as well as DC-SIGN, and suggested that the dual activities of 2G12 could be valuable in vivo for inhibiting initial virus dissemination and propagation.
Figures
References
-
- Burton DR, Pyati J, Koduri R, Sharp SJ, Thornton GB, Parren PW, Sawyer LS, Hendry RM, Dunlop N, Nara PL, et al. Efficient neutralization of primary isolates of HIV-1 by a recombinant human monoclonal antibody. Science. 1994;266:1024–1027. - PubMed
-
- Scanlan CN, Pantophlet R, Wormald MR, Saphire EO, Calarese D, Stanfield R, Wilson IA, Katinger H, Dwek RA, Burton DR, Rudd PM. The carbohydrate epitope of the neutralizing anti-HIV-1 antibody 2G12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;535:205–218. - PubMed
-
- Scanlan CN, Pantophlet R, Wormald MR, Ollmann Saphire E, Stanfield R, Wilson IA, Katinger H, Dwek RA, Rudd PM, Burton DR. The broadly neutralizing anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody 2G12 recognizes a cluster of a1-->2 mannose residues on the outer face of gp120. J Virol. 2002;76:7306–7321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.14.7306-7321.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calarese DA, Scanlan CN, Zwick MB, Deechongkit S, Mimura Y, Kunert R, Zhu P, Wormald MR, Stanfield RL, Roux KH, Kelly JW, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Katinger H, Burton DR, Wilson IA. Antibody domain exchange is an immunological solution to carbohydrate cluster recognition. Science. 2003;300:2065–2071. doi: 10.1126/science.1083182. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

