Genome-wide prediction of transcriptional regulatory elements of human promoters using gene expression and promoter analysis data
- PMID: 16817975
- PMCID: PMC1586028
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-330
Genome-wide prediction of transcriptional regulatory elements of human promoters using gene expression and promoter analysis data
Abstract
Background: A complete understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of gene expression is the next important issue of genomics. Many bioinformaticians have developed methods and algorithms for predicting transcriptional regulatory mechanisms from sequence, gene expression, and binding data. However, most of these studies involved the use of yeast which has much simpler regulatory networks than human and has many genome wide binding data and gene expression data under diverse conditions. Studies of genome wide transcriptional networks of human genomes currently lag behind those of yeast.
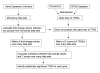
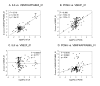
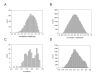
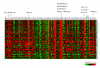
Results: We report herein a new method that combines gene expression data analysis with promoter analysis to infer transcriptional regulatory elements of human genes. The Z scores from the application of gene set analysis with gene sets of transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) were successfully used to represent the activity of TFBSs in a given microarray data set. A significant correlation between the Z scores of gene sets of TFBSs and individual genes across multiple conditions permitted successful identification of many known human transcriptional regulatory elements of genes as well as the prediction of numerous putative TFBSs of many genes which will constitute a good starting point for further experiments. Using Z scores of gene sets of TFBSs produced better predictions than the use of mRNA levels of a transcription factor itself, suggesting that the Z scores of gene sets of TFBSs better represent diverse mechanisms for changing the activity of transcription factors in the cell. In addition, cis-regulatory modules, combinations of co-acting TFBSs, were readily identified by our analysis.
Conclusion: By a strategic combination of gene set level analysis of gene expression data sets and promoter analysis, we were able to identify and predict many transcriptional regulatory elements of human genes. We conclude that this approach will aid in decoding some of the important transcriptional regulatory elements of human genes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of factors regulating gene expression in liver.Gene. 2007 Mar 15;389(2):114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.10.021. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17174484
-
Genome-wide proximal promoter analysis and interpretation.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;593:157-74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-194-3_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19957149
-
FactorY, a bioinformatic resource for genome-wide promoter analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2009 Apr;39(4):385-7. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.01.008. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Comput Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 19272592
-
Genome-wide location analysis: insights on transcriptional regulation.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Apr 15;15 Spec No 1:R1-7. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl043. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16651365 Review.
-
Computational biology: toward deciphering gene regulatory information in mammalian genomes.Biometrics. 2006 Sep;62(3):645-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2006.00625.x. Biometrics. 2006. PMID: 16984301 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a novel prediction method of cis-elements to hypothesize collaborative functions of cis-element pairs in iron-deficient rice.Rice (N Y). 2013 Sep 22;6(1):22. doi: 10.1186/1939-8433-6-22. Rice (N Y). 2013. PMID: 24279975 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory gene regulatory networks in amnion cells following cytokine stimulation: translational systems approach to modeling human parturition.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020560. Epub 2011 Jun 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21655103 Free PMC article.
-
Gene set-based module discovery decodes cis-regulatory codes governing diverse gene expression across human multiple tissues.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 9;5(6):e10910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010910. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20544005 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide transcription factor binding site/promoter databases for the analysis of gene sets and co-occurrence of transcription factor binding motifs.BMC Genomics. 2010 Mar 1;11:145. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-145. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20193056 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis: evaluation of response intensities--tailoring ANOVA for lists of expression subsets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Oct 13;11:510. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-510. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20942918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Robert F, Odom DT, Bar-Joseph Z, Gerber GK, Hannett NM, Harbison CT, Thompson CM, Simon I, Zeitlinger J, Jennings EG, Murray HL, Gordon DB, Ren B, Wyrick JJ, Tagne JB, Volkert TL, Fraenkel E, Gifford DK, Young RA. Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 2002;298:799–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1075090. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

