Con-nectin axons and dendrites
- PMID: 16818715
- PMCID: PMC2064153
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200606024
Con-nectin axons and dendrites
Abstract
Unlike adherens junctions, synapses are asymmetric connections, usually between axons and dendrites, that rely on various cell adhesion molecules for structural stability and function. Two cell types of adhesion molecules found at adherens junctions, cadherins and nectins, are thought to mediate homophilic interaction between neighboring cells. In this issue, Togashi et al. (see p. 141) demonstrate that the differential localization of two heterophilic interacting nectins mediates the selective attraction of axons and dendrites in cooperation with cadherins.
Figures
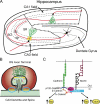
Comment on
-
Interneurite affinity is regulated by heterophilic nectin interactions in concert with the cadherin machinery.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul 3;174(1):141-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601089. Epub 2006 Jun 26. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16801389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayer, S.A. 1980. Development of the hippocampal region in the rat. I. Neurogenesis examined with 3H-thymidine autoradiography. J. Comp. Neurol. 190:87–114. - PubMed
-
- Gumbiner, B.M. 2005. Regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:622–634. - PubMed
-
- Hatzfeld, M. 2005. The p120 family of cell adhesion molecules. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 84:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Honda, T., T. Sakisaka, T. Yamada, N. Kumazawa, T. Hoshino, M. Kajita, T. Kayahara, H. Ishizaki, M. Tanaka-Okamoto, A. Mizoguchi, et al. 2006. Involvement of nectins in the formation of puncta adherentia junctions and the mossy fiber trajectory in the mouse hippocampus. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 31:315–325. - PubMed

