COPII-Golgi protein interactions regulate COPII coat assembly and Golgi size
- PMID: 16818719
- PMCID: PMC2064162
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200604058
COPII-Golgi protein interactions regulate COPII coat assembly and Golgi size
Abstract
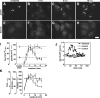
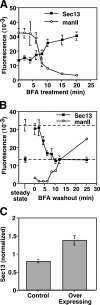
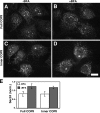
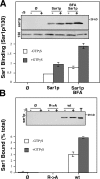
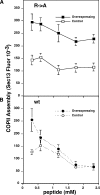
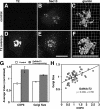
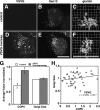
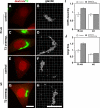
Under experimental conditions, the Golgi apparatus can undergo de novo biogenesis from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), involving a rapid phase of growth followed by a return to steady state, but the mechanisms that control growth are unknown. Quantification of coat protein complex (COP) II assembly revealed a dramatic up-regulation at exit sites driven by increased levels of Golgi proteins in the ER. Analysis in a permeabilized cell assay indicated that up-regulation of COPII assembly occurred in the absence GTP hydrolysis and any cytosolic factors other than the COPII prebudding complex Sar1p-Sec23p-Sec24p. Remarkably, acting via a direct interaction with Sar1p, increased expression of the Golgi enzyme N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase-2 induced increased COPII assembly on the ER and an overall increase in the size of the Golgi apparatus. These results suggest that direct interactions between Golgi proteins exiting the ER and COPII components regulate ER exit, providing a variable exit rate mechanism that ensures homeostasis of the Golgi apparatus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sit4p/PP6 regulates ER-to-Golgi traffic by controlling the dephosphorylation of COPII coat subunits.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Sep;24(17):2727-38. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-02-0114. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23864707 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of COPII vesicles and the Golgi apparatus in cultured Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells provides evidence for transient association of Golgi stacks with endoplasmic reticulum exit sites.Plant Cell. 2005 May;17(5):1513-31. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026757. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Plant Cell. 2005. PMID: 15805489 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum export sites and Golgi bodies behave as single mobile secretory units in plant cells.Plant Cell. 2004 Jul;16(7):1753-71. doi: 10.1105/tpc.022673. Epub 2004 Jun 18. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15208385 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle-mediated export from the ER: COPII coat function and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1833(11):2464-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23419775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COPII-coated vesicles: flexible enough for large cargo?Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;17(4):345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.06.004. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15975775 Review.
Cited by
-
Coat-tether interaction in Golgi organization.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jul;19(7):2830-43. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1236. Epub 2008 Apr 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18434597 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro vesicle formation assay reveals cargo clients and factors that mediate vesicular trafficking.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 31;118(35):e2101287118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101287118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34433667 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of coat assembly--sorting things out at the ER.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;22(4):447-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 May 1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20439155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Who needs microtubules? Myogenic reorganization of MTOC, Golgi complex and ER exit sites persists despite lack of normal microtubule tracks.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029057. Epub 2011 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22216166 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of EGFR surface levels by COPII-dependent trafficking.J Cell Biol. 2016 Nov 21;215(4):441-443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201611014. Epub 2016 Nov 8. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27872251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonny, B., D. Madden, S. Hamamoto, L. Orci, and R. Schekman. 2001. Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTP and stable analogues. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Aridor, M., and L.M. Traub. 2002. Cargo selection in vesicular transport: the making and breaking of a coat. Traffic. 3:537–546. - PubMed
-
- Aridor, M., S.I. Bannykh, T. Rowe, and W.E. Balch. 1999. Cargo can modulate COPII vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 274:4389–4399. - PubMed

