Agonist ligands expressed by thymic epithelium enhance positive selection of regulatory T lymphocytes from precursors with a normally diverse TCR repertoire
- PMID: 16818767
- PMCID: PMC2346540
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1101
Agonist ligands expressed by thymic epithelium enhance positive selection of regulatory T lymphocytes from precursors with a normally diverse TCR repertoire
Abstract
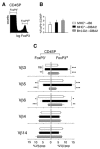
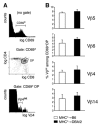
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes play a crucial role in inhibition of autoimmune pathology. In accordance with this physiological role, it is now well established that the repertoire of these lymphocytes is strongly enriched in autospecific cells. However, despite extensive investigation, the thymic mechanisms involved in development of regulatory T cells remain incompletely defined. To address the issue of selection of regulatory T cell precursors in mice with a naturally diverse TCR repertoire, we have analyzed development of superantigen-specific regulatory T cells in hemopoietic chimeras in which endogenous super-antigens are exclusively presented by thymic epithelial cells. Our results demonstrate that recognition of agonist ligands expressed by thymic epithelium does not lead to deletion but substantially enhances development of mature regulatory T cells. Interestingly, also development of a small subpopulation of CD25-expressing T cells lacking expression of the transcription factor Foxp3, thought to be autospecific, is enhanced by expression of the agonist ligand on thymic epithelium. Based on quantitative arguments, we propose that commitment to the regulatory T cell lineage is not dictated by the specificity of precursors, but that recognition of the agonist ligand expressed by thymic epithelium substantially enhances their positive selection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Peptide specificity of thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ T cells.J Immunol. 2002 Jan 15;168(2):613-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.2.613. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11777953
-
Shaping of the autoreactive regulatory T cell repertoire by thymic cortical positive selection.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):6741-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6741. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982064 Free PMC article.
-
Ikaros null mice display defects in T cell selection and CD4 versus CD8 lineage decisions.J Immunol. 2004 Oct 1;173(7):4470-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4470. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15383578
-
Thymic commitment of regulatory T cells is a pathway of TCR-dependent selection that isolates repertoires undergoing positive or negative selection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;293:43-71. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27702-1_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981475 Review.
-
Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells: Key Developers of the Code of T-Cell Selection and TCR Repertoire Diversity.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jul;332(1):e70049. doi: 10.1111/imr.70049. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40558027 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved and divergent aspects of human T-cell development and migration in humanized mice.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;93(8):716-26. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.38. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25744551 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cells in the thymus contribute to T-regulatory cell induction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 16;105(50):19869-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810268105. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19073916 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses to endogenous retroelements: taking the bad with the good.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Apr;16(4):207-19. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.27. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27026073 Review.
-
Hematopoietic chimerism and transplantation tolerance: a role for regulatory T cells.Front Immunol. 2011 Dec 28;2:80. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00080. eCollection 2011. Front Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22566869 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial and dendritic cells in the thymic medulla promote CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell development via the CD27-CD70 pathway.J Exp Med. 2013 Apr 8;210(4):715-28. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112061. Epub 2013 Apr 1. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23547099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hogquist KA, Baldwin TA, Jameson SC. Central tolerance: learning self-control in the thymus. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:772–782. - PubMed
-
- Bouneaud C, Kourilsky P, Bousso P. Impact of negative selection on the T cell repertoire reactive to a self-peptide: A large fraction of T cell clones escapes clonal deletion. Immunity. 2000;13:829–840. - PubMed
-
- Stockinger B. T lymphocyte tolerance: from thymic deletion to peripheral control mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1999;71:229–265. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

