Reconstitution of invertebrate glutamate receptor function depends on stargazin-like proteins
- PMID: 16818877
- PMCID: PMC1502308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604482103
Reconstitution of invertebrate glutamate receptor function depends on stargazin-like proteins
Abstract
alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors (AMPARs) are a major subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) that mediate rapid excitatory synaptic transmission in the vertebrate brain. Putative AMPARs are also expressed in the nervous system of invertebrates. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the GLR-1 receptor subunit is expressed in neural circuits that mediate avoidance behaviors and is required for glutamate-gated current in the AVA and AVD interneurons. Glutamate-gated currents can be recorded from heterologous cells that express vertebrate AMPARs; however, when C. elegans GLR-1 is expressed in heterologous cells, little or no glutamate-gated current is detected. This finding suggests that other receptor subunits or auxiliary proteins are required for function. Here, we identify Ce STG-1, a C. elegans stargazin-like protein, and show that expression of Ce STG-1 together with GLR-1 and the CUB-domain protein SOL-1 reconstitutes glutamate-gated currents in Xenopus oocytes. Ce STG-1 and homologues cloned from Drosophila (Dro STG1) and Apis mellifera (Apis STG1) have evolutionarily conserved functions and can partially substitute for one another to reconstitute glutamate-gated currents from rat, Drosophila, and C. elegans. Furthermore, we show that Ce STG-1 and Apis STG1 are primarily required for function independent of possible roles in promoting the surface expression of invertebrate AMPARs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
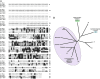
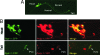
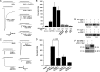
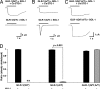

Similar articles
-
Conserved SOL-1 proteins regulate ionotropic glutamate receptor desensitization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 11;103(28):10787-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604520103. Epub 2006 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16818875 Free PMC article.
-
SOL-1 is an auxiliary subunit that modulates the gating of GLR-1 glutamate receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 24;103(4):1100-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504612103. Epub 2006 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16418277 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate receptor subunits by domain transplantation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):44691-701. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305497200. Epub 2003 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12930835
-
Ionotropic glutamate receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans.Neurosignals. 2003 May-Jun;12(3):108-25. doi: 10.1159/000072159. Neurosignals. 2003. PMID: 12904685 Review.
-
Building a synapse: genetic analysis of glutamatergic neurotransmission.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):64-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0340064. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16417484 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Activity and CaMKII Regulate Kinesin-Mediated Transport of Synaptic AMPARs.Neuron. 2015 Apr 22;86(2):457-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25843407 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Conus snail polypeptide causes excitotoxicity by blocking desensitization of AMPA receptors.Curr Biol. 2009 Jun 9;19(11):900-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.017. Epub 2009 May 28. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19481459 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the interaction sites between AMPA receptors and TARPs reveals a role for the receptor N-terminal domain in channel gating.Cell Rep. 2014 Oct 23;9(2):728-40. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.029. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25373908 Free PMC article.
-
Functional reconstitution of Drosophila melanogaster NMJ glutamate receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):6182-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500458112. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25918369 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted Amyloid Precursor Protein Alpha, a Neuroprotective Protein in the Brain Has Widespread Effects on the Transcriptome and Proteome of Human Inducible Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Glutamatergic Neurons Related to Memory Mechanisms.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 26;16:858524. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.858524. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35692428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dingledine R., Borges K., Bowie D., Traynelis S. F. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
-
- Hollmann M., O’Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Nature. 1989;342:643–648. - PubMed
-
- Hart A. C., Sims S., Kaplan J. M. Nature. 1995;378:82–85. - PubMed
-
- Maricq A. V., Peckol E., Driscoll M., Bargmann C. I. Nature. 1995;378:78–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

