Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a marker of germinal center-associated T cells and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 16819321
- PMCID: PMC3137919
- DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000209855.28282.ce
Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a marker of germinal center-associated T cells and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
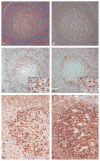
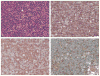
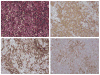
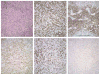
Programmed death-1 (PD-1), a member of the CD28 costimulatory receptor family, is expressed by germinal center-associated T cells in reactive lymphoid tissue. In a study of a wide range of lymphoproliferative disorders, neoplastic T cells in 23 cases of angioimmunoblastic lymphoma were immunoreactive for PD-1, but other subtypes of T cell and B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, as well as classic Hodgkin lymphoma, did not express PD-1. The pattern of PD-1 immunostaining of neoplastic cells in angioimmunoblastic lymphoma was similar to that reported for CD10, a recently described marker of neoplastic T cells in angioimmunoblastic lymphoma. Tumor-associated follicular dendritic cells in cases of angioimmunoblastic lymphoma were found to express PD-L1, the PD-1 ligand. In addition, PD-1-positive reactive T cells formed rosettes around neoplastic L&H cells in 14 cases of nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma studied. These findings, along with data from previous studies, suggest that angioimmunoblastic lymphoma is a neoplasm of germinal center-associated T cells and that there is an association of germinal center-associated T cells and neoplastic cells in nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. PD-1 is a useful new marker for angioimmunoblastic lymphoma and lends further support to a model of T-cell lymphomagenesis in which specific subtypes of T cells may undergo neoplastic transformation and result in specific, distinct histologic, immunophenotypic, and clinical subtypes of T-cell neoplasia.
Figures
References
-
- Riley JL, June CH. The CD28 family: a T-cell rheostat for therapeutic control of T-cell activation. Blood. 2005;105:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. The B7-CD28 superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:116–126. - PubMed
-
- Probst HC, McCoy K, Okazaki T, et al. Resting dendritic cells induce peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance through PD-1 and CTLA-4. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:280–286. - PubMed
-
- Brown J, Dorfman DM, Ma F-R, et al. Blockade of PD-1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J Immunol. 2003;170:1257–1266. - PubMed
-
- Iwai Y, Okaszaki T, Nishimura H, et al. Microanatomical localization of PD-1 in human tonsils. Immunol Lett. 2002;83:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

